- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄376462 > XRT75R06IB (EXAR CORP) SIX CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER ATTENUATOR PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | XRT75R06IB |
| 廠商: | EXAR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 數(shù)字傳輸電路 |
| 英文描述: | SIX CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER ATTENUATOR |
| 中文描述: | DATACOM, PCM TRANSCEIVER, PBGA217 |
| 封裝: | 23 X 23 MM, BGA-217 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 40/63頁 |
| 文件大小: | 350K |
| 代理商: | XRT75R06IB |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁當(dāng)前第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁
XRT75R06
REV. 1.0.0
á
SIX CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER ATTENUATOR
37
5.2
Jitter Transfer function is defined as the ratio of jitter on the output relative to the jitter applied on the input
versus frequency. There are two distinct characteristics in jitter transfer, jitter gain (jitter peaking) defined as
the highest ratio above 0dB and jitter transfer bandwidth. The overall jitter transfer bandwidth is controlled by a
low bandwidth loop, typically using a voltage-controlled crystal oscillator (VCXO).
The jitter transfer function is a ratio between the jitter output and jitter input for a component, or system often
expressed in dB. A negative dB jitter transfer indicates the element removed jitter. A positive dB jitter transfer
indicates the element added jitter. A zero dB jitter transfer indicates the element had no effect on jitter. Table 9
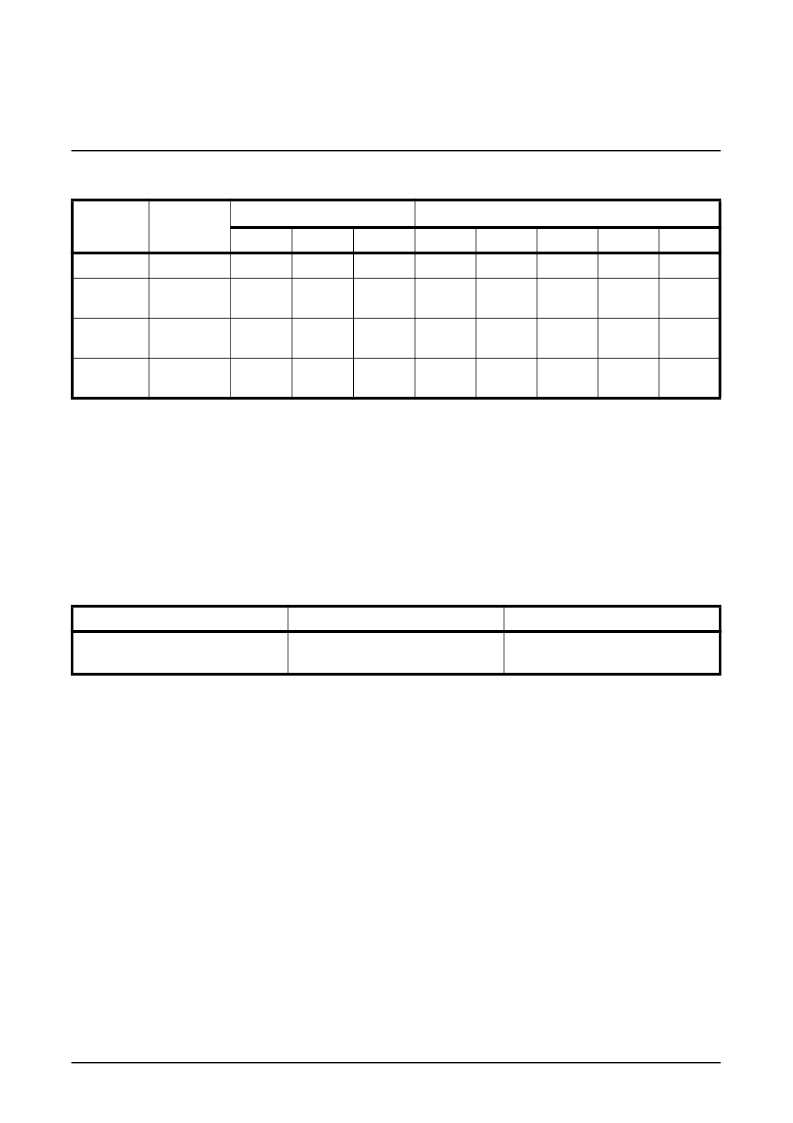
shows the jitter transfer characteristics and/or jitter attenuation specifications for various data rates:
J
ITTER
T
RANSFER
N
OTE
:
The above specifications can be met only with a jitter attenuator that supports E3/DS3/STS-1 rates.
5.3
Jitter Attenuator
An advanced crystal-less jitter attenuator per channel is included in the XRT75R06. The jitter attenuator
requires no external crystal nor high-frequency reference clock. By clearing or setting the JATx/Rx_n bits in
the channel control registers selects the jitter attenuator either in the Receive or Transmit path on per channel
basis. The FIFO size can be either 16-bit or 32-bit. The bits JA0_n and JA1_n can be set to appropriate
combination to select the different FIFO sizes or to disable the Jitter Attenuator on a per channel basis. Data is
clocked into the FIFO with the associated clock signal (TxClk or RxClk) and clocked out of the FIFO with the
dejittered clock. When the FIFO is within two bits of overflowing or underflowing, the FIFO limit status bit, FL_n
is set to “1” in the Alarm status register. Reading this bit clears the FIFO and resets the bit into default state.
N
OTE
:
It is recommended to select the 16-bit FIFO for delay-sensitive applications as well as for removing smaller amounts
of jitter. Table 10 specifies the jitter transfer mask requirements for various data rates:
T
ABLE
8: J
ITTER
A
MPLITUDE
VERSUS
M
ODULATION
F
REQUENCY
(J
ITTER
T
OLERANCE
)
B
IT
R
ATE
(
KB
/
S
)
S
TANDARD
I
NPUT
J
ITTER
A
MPLITUDE
(UI
P
-
P
)
M
ODULATION
F
REQUENCY
A1
A2
A3
F
1(H
Z
)
F
2(H
Z
)
F
3(
K
H
Z
)
F
4(
K
H
Z
)
F
5(
K
H
Z
)
34368
ITU-T G.823
1.5
0.15
-
100
1000
10
800
-
44736
GR-499
CORE Cat I
5
0.1
-
10
2.3k
60
300
-
44736
GR-499
CORE Cat II
10
0.3
-
10
669
22.3
300
-
51840
GR-253
CORE Cat II
15
1.5
0.15
10
30
300
2
20
T
ABLE
9: J
ITTER
T
RANSFER
S
PECIFICATION
/R
EFERENCES
E3
DS3
STS-1
ETSI TBR-24
GR-499 CORE section 7.3.2
Category I and Category II
GR-253 CORE section 5.6.2.1
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XRT75R12D | TWELVE CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH SONET DESYNCHRONIZER |
| XRT75R12DIB | TWELVE CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH SONET DESYNCHRONIZER |
| XRT75R12 | TWELVE CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER ATTENUATOR |
| XRT75R12IB | TWELVE CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER ATTENUATOR |
| XRT75VL00 | E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER ATTENUATOR |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XRT75R06IB208 | 制造商:Exar Corporation 功能描述:Line Interface Unit 51.84Mbps DS3/E3/STS-1 Parallel 217-Pin BGA |
| XRT75R06IB-F | 功能描述:外圍驅(qū)動(dòng)器與原件 - PCI 6 Channel 3.3V-5V temp -45 to 85C RoHS:否 制造商:PLX Technology 工作電源電壓: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:FCBGA-1156 封裝:Tray |
| XRT75R12 | 制造商:EXAR 制造商全稱:EXAR 功能描述:TWELVE CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER |
| XRT75R12_07 | 制造商:EXAR 制造商全稱:EXAR 功能描述:TWELVE CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER |
| XRT75R12_0710 | 制造商:EXAR 制造商全稱:EXAR 功能描述:TWELVE CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH JITTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。