- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄377999 > MR2900 (Shindengen Electric Manufacturing Company, Ltd.) Provision for Standby mode operation Partial Resonance Power Supply IC Module PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MR2900 |
| 廠商: | Shindengen Electric Manufacturing Company, Ltd. |
| 英文描述: | Provision for Standby mode operation Partial Resonance Power Supply IC Module |
| 中文描述: | 撥備待機(jī)模式操作局部共振電源IC模塊 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 6/19頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 226K |
| 代理商: | MR2900 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)當(dāng)前第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)
Shindengen Electric MFG.CO.,LTD
- 6 -
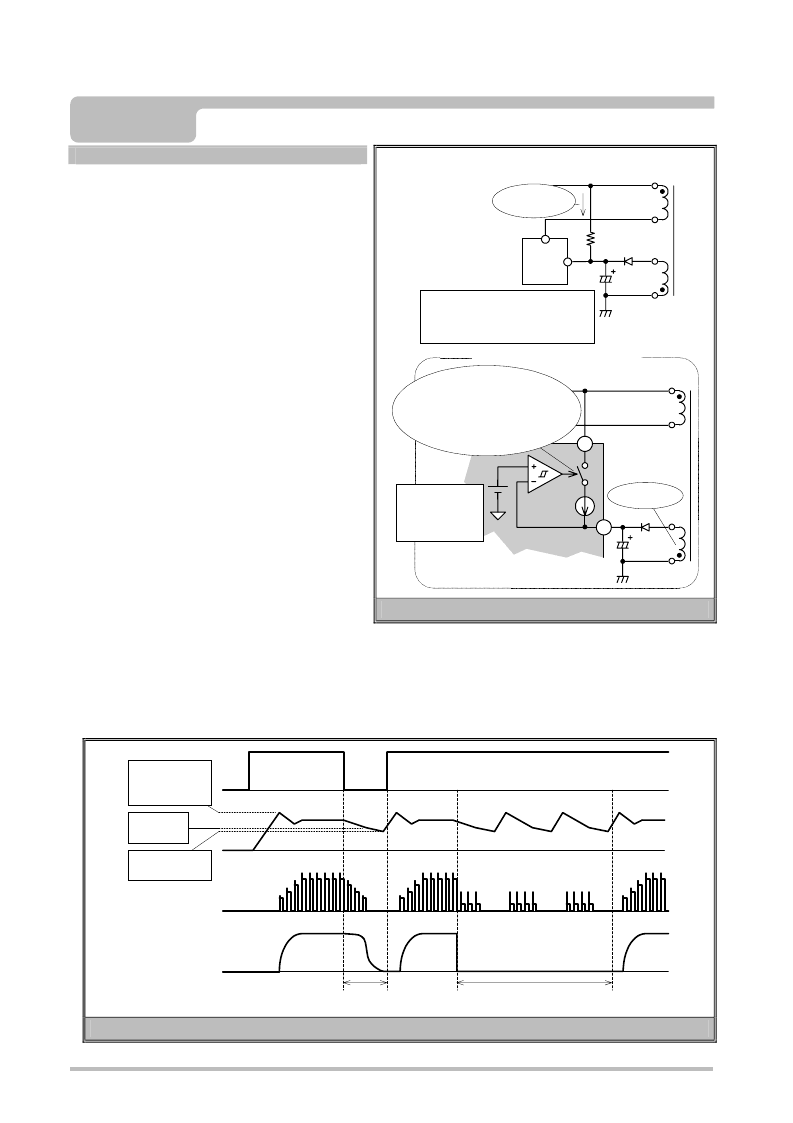
3.1 Start-up Circuit
In conventional start-up circuits employing a start-up
resistor, current continues to flow following power supply
start-up, thus wasting power and reducing efficiency,
particularly during standby.
See Fig.3.1 Comparison of Start-up Circuits - Conventional
Start-up Circuit.
In the MR2000 Series start-up circuit the start-up current is
supplied from the input voltage at power supply start-up,
and is shut-off when the power supply is in operation.
The start-up circuit supplies a current of 12mA (typical) from
the IC internal constant current source until the voltage at
the V
cc
pin reaches 14V (typical). This current is consumed
internally in the IC as well as being used as the charging
current for the condenser connected externally between the
V
cc
pin and GND.
This design allows a stable start-up only minimally
dependent upon input voltage.
When the voltage at the V
cc
pin reaches 14V (typical) the
start-up circuit is disconnected, the start-up current no
longer flows and oscillation begins simultaneously.
The current consumed in the IC is then supplied from the
control coil. See Fig.3.1 Comparison of Start-up Circuits -
MR2000 Start-up Circuit.
In the case of an instantaneous power failure or a load
short, oscillation is stopped when the voltage at the V
cc
pin reaches 8.5V, and when this voltage drops to 7.6V the start-up circuit
operates again and the voltage at the V
cc
pin then begins rising. See Fig.3.2.
Incorporation of the functions described above improve efficiency, particularly during standby, and reduces the number of start-up
resistors required, thus reducing the overall number of components.
Fig.3.1 Comparison of Start-up Circuits
Fig.3.2 Start-up Circuit Operation Sequence
3. Operation Description
MR2900
Application Note
Load short
Instantaneous power failure
【
V
OUT
】
V
CC(startup on)
=7.6V
【
V
CE
】
V
CC(stop)
=8.5V
V
CC(startup off)
=
V
CC(Start)
=14.0V
【
V
CC
】
【
Vin
】
Vcc pin
Vin pin
5
4
V
cc(startup off)
/V
cc(startup on)
14.5V/7.2V
【
MR2000 Start-up Circuit
】
Control coil
Start-up current switched off
following start-up, thus
eliminating the need for start-up
resistors.
【
Conventional Start-up Circuit
】
IC
Start-up
current
Start-up current flows even
during steady-state operation,
resulting in losses.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MR2920 | Provision for Standby mode operation Partial Resonance Power Supply IC Module |
| MR2940 | Provision for Standby mode operation Partial Resonance Power Supply IC Module |
| MS52C181A | 131,072-Word × 8-Bit STATIC RAM +1,048,576-Word × 8-Bit One Time PROM(128k字×8位靜態(tài)RAM+1M字×8位 OTPROM) |
| MS52C182A | 65,536-Word × 16-Bit or 131,072-Word × 8-Bit STATIC RAM +524,288-Word × 16-Bit or 1,048,576-Word × 8-Bit One Time PROM(64k字×16位或128k字×8位靜態(tài)RAM+512k字×16位或1M字×8位 OTPROM) |
| MS81V06160 | (401,408-word ⅴ 16-bit) FIFO memory |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MR29-0R2011 | 制造商:Alpha 3 Manufacturing 功能描述: |
| MR29-0R2022 | 制造商:Alpha 3 Manufacturing 功能描述: |
| MR29-0R2223 | 制造商:Alpha 3 Manufacturing 功能描述: |
| MR29-0R2227 | 制造商:Alpha 3 Manufacturing 功能描述: |
| MR291.04D | 制造商:IVO 制造商全稱(chēng):Baumer IVO GmbH & Co. KG 功能描述:Accessories & Service |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。