- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98158 > TAS3103DBTRG4 (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDSO38 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | TAS3103DBTRG4 |
| 廠商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 消費家電 |
| 英文描述: | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDSO38 |
| 封裝: | GREEN, PLASTIC, TSSOP-38 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/148頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1247K |
| 代理商: | TAS3103DBTRG4 |
第1頁第2頁當前第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁
341
When T1 and T2 are set equal, the following questions arise:
If O1
≠ O2, what roles do O1 and O2 have?
Which slope parameter, k0 or k1, has control of the transfer function for input levels below the common
threshold point?
Does k2 control the transfer function for inputs above the common threshold point?
This example addresses and answers those questions.
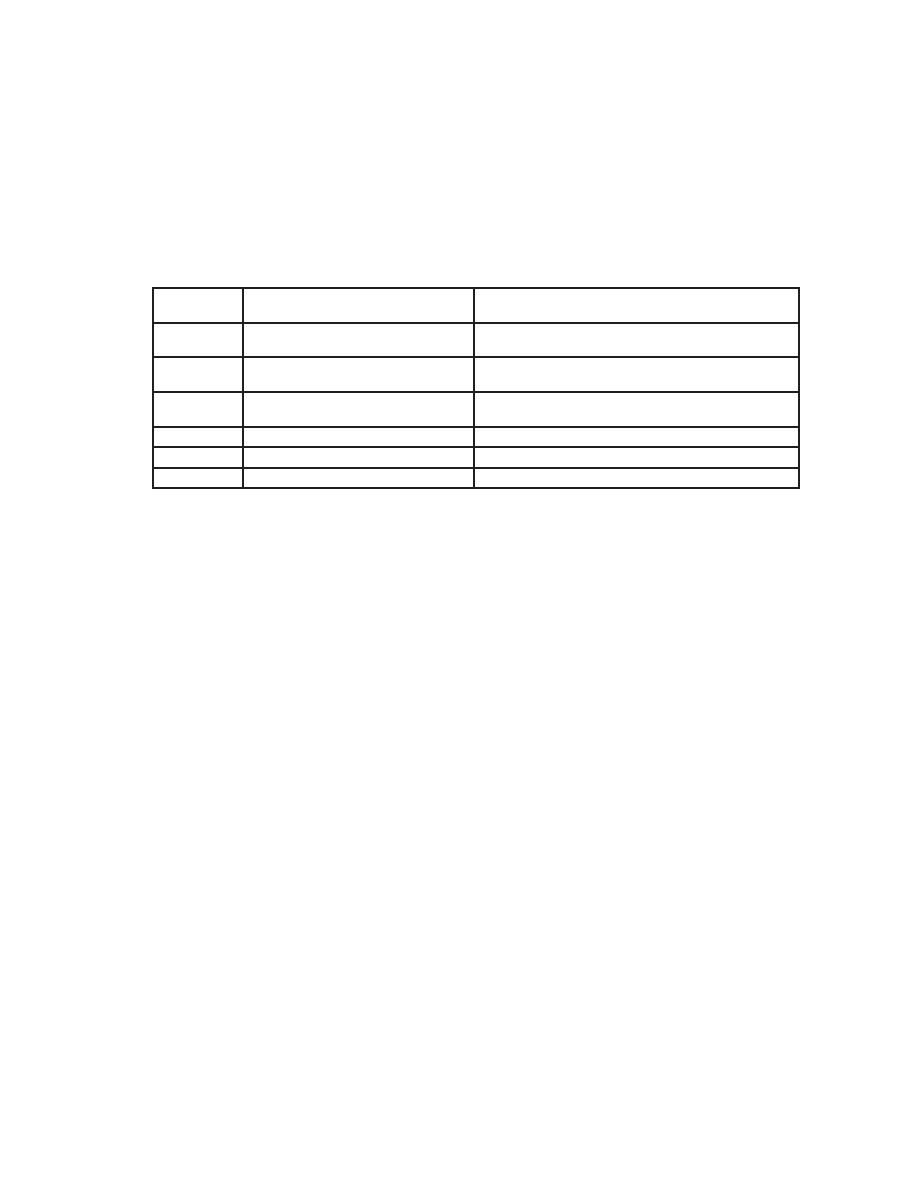
Table 36. DRC Example 3 Parameters
DRC
PARAMETER
REQUIRED (SPECIFIED) VALUE
(NET GAINSAP Input-DRC = 0 dB)
I2C COEFFICIENT VALUE
T1 and T2
148.7 dBInput ≥ 172.7 dBDRC
172.7/6.0206 = 28.684849
= 0x00000E57A91F25.23 Format
O2
20 dB
(20 + 24.0824)/6.0206 = 0.678072
= 0x00000056CB0F25.23 Format
O1
10 dB
(10 + 24.0824)/6.0206 = 5.660964
= 0x000002D49A7825.23 Format
k2
∞:1 Compression
(1/
∞) 1 = 1 = 0xF8000005.23 Format
k1
1:1 Transfer
(1/1) 1 = 0 = 0x00000005.23 Format
k0
2:1 Compression
(1/2) 1 = 0.5 = 0xFC000005.23 Format
For this example it is assumed that a net processing gain of 24 (24 dB) is realized from the SAP input and the DRC
(which is identical to the net processing gain assumed for Example 1). The 24 gain results in reducing the 8-bit
headroom in the 48-bit DAP word to a headroom of four bits. The 32-bit data into the DRC then resides in bits 27:0,
which means that the data level into the DRC is down 24 dB with respect to the input level at the SAP. Data input into
the TAS3103 (SAP) at a level of 148.7 dB is seen as a 148.7 dB 24 dB = 172.7-dB signal at the DRC. T1 and
T2 must be set to 172.7 dB to realize a common threshold point at an incoming signal level of 148.7 dB.
Figure 325 shows the transfer function resulting from entering the I2C coefficient values given in Table 36. At the
T1/T2 threshold, a discontinuity of 30 dB is observed. For inputs above the threshold, the transfer curve is horizontal
(infinite compression), and the horizontal line starts 20 dB above the 1:1 transfer curve at the threshold point. Thus,
for cases when T1 = T2, O2 governs the offset with regard to the starting point of the transfer curve above the common
threshold point and k2 determines the slope of the transfer curve. For inputs below the common threshold point, the
transfer curve exhibits a 2:1 compression and starts 10 dB below the 1:1 transfer curve. Thus, O1 sets the offset at
the threshold point for the transfer curve at and below the common threshold point and k0 determines the slope of
this curve. Slope parameter k1 plays no role when T1 = T2. The value of 0 (1:1 transfer) used in this example for k1
could be changed to any value and the resulting transfer function would not be altered. The change from a 2:1
compression to a 1:1 transfer at 192 dB is due to 32-bit dynamic range saturation at the DRC input.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TAS3103DBTR | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDSO38 |
| TAS3103IDBTRG4 | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDSO38 |
| TAS3103IDBTR | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDSO38 |
| TAS3103IDCP | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDSO38 |
| TAS3103DBTG4 | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDSO38 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TAS3103EVM | 功能描述:音頻 DSP TAS3103 Eval Mod RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 工作電源電壓: 電源電流: 工作溫度范圍: 安裝風格: 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Tube |
| TAS3103IDBT | 功能描述:音頻 DSP Digital Audio Processor RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 工作電源電壓: 電源電流: 工作溫度范圍: 安裝風格: 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Tube |
| TAS3103IDBTR | 功能描述:音頻 DSP Digital Audio Processor RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 工作電源電壓: 電源電流: 工作溫度范圍: 安裝風格: 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Tube |
| TAS3103IDBTRG4 | 功能描述:音頻 DSP Digital Audio Processor RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 工作電源電壓: 電源電流: 工作溫度范圍: 安裝風格: 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Tube |
| TAS3108 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:AUDIO DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。