- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4277 > XC2S150-6FG456C (Xilinx Inc)IC FPGA 2.5V C-TEMP 456-FBGA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | XC2S150-6FG456C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 11/99頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 2.5V C-TEMP 456-FBGA |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 60 |
| 系列: | Spartan®-II |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 864 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 3888 |
| RAM 位總計: | 49152 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 260 |
| 門數(shù): | 150000 |
| 電源電壓: | 2.375 V ~ 2.625 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 456-BBGA |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 456-FBGA |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁當(dāng)前第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁
Spartan-II FPGA Family: Functional Description
DS001-2 (v2.8) June 13, 2008
Module 2 of 4
Product Specification
19
R
Clearing Configuration Memory
The device indicates that clearing the configuration memory
is in progress by driving INIT Low. At this time, the user can
delay configuration by holding either PROGRAM or INIT
Low, which causes the device to remain in the memory
clearing phase. Note that the bidirectional INIT line is
driving a Low logic level during memory clearing. To avoid
contention, use an open-drain driver to keep INIT Low.
With no delay in force, the device indicates that the memory
is completely clear by driving INIT High. The FPGA samples
its mode pins on this Low-to-High transition.
Loading Configuration Data
Once INIT is High, the user can begin loading configuration
data frames into the device. The details of loading the
configuration data are discussed in the sections treating the
configuration modes individually. The sequence of
operations necessary to load configuration data using the
serial modes is shown in Figure 14. Loading data using the
Slave Parallel mode is shown in Figure 19, page 25.
CRC Error Checking
During the loading of configuration data, a CRC value
embedded in the configuration file is checked against a
CRC value calculated within the FPGA. If the CRC values
do not match, the FPGA drives INIT Low to indicate that a
frame error has occurred and configuration is aborted.
To reconfigure the device, the PROGRAM pin should be
asserted to reset the configuration logic. Recycling power
also resets the FPGA for configuration. See "Clearing
Start-up
The start-up sequence oversees the transition of the FPGA
from the configuration state to full user operation. A match
of CRC values, indicating a successful loading of the
configuration data, initiates the sequence.
During start-up, the device performs four operations:
1.
The assertion of DONE. The failure of DONE to go High
may indicate the unsuccessful loading of configuration
data.
2.
The release of the Global Three State net. This
activates I/Os to which signals are assigned. The
remaining I/Os stay in a high-impedance state with
internal weak pull-down resistors present.
3.
Negates Global Set Reset (GSR). This allows all
flip-flops to change state.
4.
The assertion of Global Write Enable (GWE). This
allows all RAMs and flip-flops to change state.
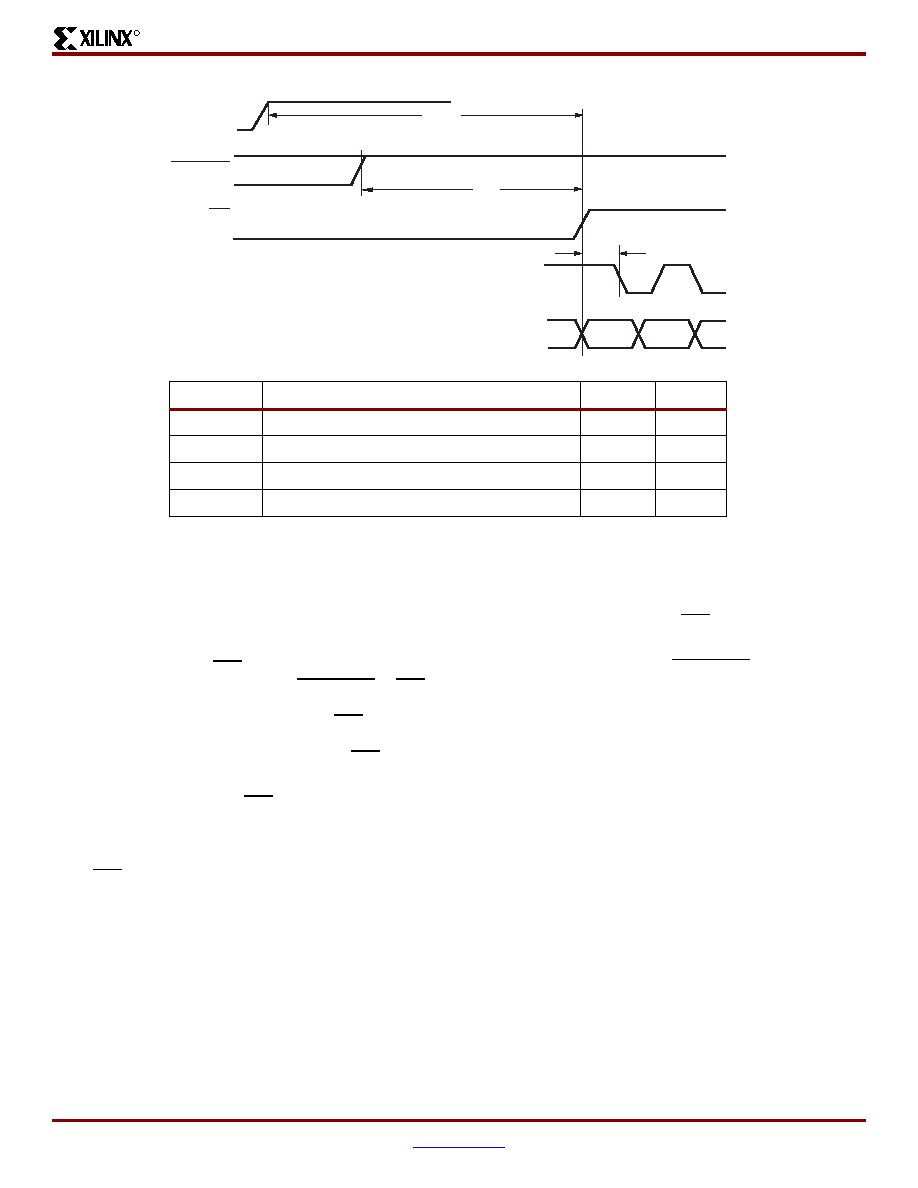
Notes: (referring to waveform above:)
1.
Before configuration can begin, VCCINT must be greater than 1.6V and VCCO Bank 2 must be greater than 1.0V.
Figure 12: Configuration Timing on Power-Up
DS001_12_102301
TPOR
TPL
TICCK
Valid
CCLK Output or Input
M0, M1, M2
(Required)
PROGRAM
INIT
VCC(1)
.
Symbol
Description
Min
Max
TPOR
Power-on reset
-
2 ms
TPL
Program latency
-
100
μs
TICCK
CCLK output delay (Master Serial mode only)
0.5
μs4 μs
TPROGRAM
Program pulse width
300 ns
-
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 745530-3 | CONN BACK COVER SLIDE ON DB25 |
| 93AA86A-I/MS | IC EEPROM 16KBIT 2048X8 8-MSOP |
| XC2S150-5FG456I | IC FPGA 2.5V I-TEMP 456-FBGA |
| XC3S500E-4FG320I | IC FPGA SPARTAN 3E 320FBGA |
| 25LC040AT-I/MNY | IC EEPROM SER 4K 512X8 8TDFN |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XC2S150-6FG456I | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述: |
| XC2S150-6FGG256C | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述:FPGA SPARTAN-II 150K GATES 3888 CELLS 263MHZ 2.5V 256FBGA - Trays 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述:FPGA, 864 CLBS, 150000 GATES, 263 MHz, PBGA256 |
| XC2S150-6FGG256I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-II FPGA Family |
| XC2S150-6FGG456C | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述:FPGA SPARTAN-II 150K GATES 3888 CELLS 263MHZ 2.5V 456FBGA - Trays 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述:IC FPGA 260 I/O 456FBGA 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述:IC FPGA SPARTAN-2C 150K 456FBGA |
| XC2S150-6FGG456I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Spartan-II FPGA Family |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。