- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4220 > XCV405E-6FG676I (Xilinx Inc)IC FPGA 1.8V 676-BGA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | XCV405E-6FG676I |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 43/118頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 1.8V 676-BGA |
| 產(chǎn)品變化通告: | FPGA Family Discontinuation 18/Apr/2011 |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 1 |
| 系列: | Virtex®-E EM |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 2400 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 10800 |
| RAM 位總計(jì): | 573440 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 404 |
| 門(mén)數(shù): | 129600 |
| 電源電壓: | 1.71 V ~ 1.89 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | -40°C ~ 100°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 676-BGA |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 676-FBGA(27x27) |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)當(dāng)前第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)
Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays
Module 2 of 4
DS025-2 (v3.0) March 21, 2014
26
R
— OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE —
Port Signals
Each block SelectRAM+ port operates independently of the
others while accessing the same set of 4096 memory cells.
Table 15 describes the depth and width aspect ratios for the
block SelectRAM+ memory.
Clock—CLK[A|B]
Each port is fully synchronous with independent clock pins.
All port input pins have setup time referenced to the port
CLK pin. The data output bus has a clock-to-out time refer-
enced to the CLK pin.
Enable—EN[A|B]
The enable pin affects the read, write and reset functionality
of the port. Ports with an inactive enable pin keep the output
pins in the previous state and do not write data to the mem-
ory cells.
Write Enable—WE[A|B]
Activating the write enable pin allows the port to write to the
memory cells. When active, the contents of the data input
bus are written to the RAM at the address pointed to by the
address bus, and the new data also reflects on the data out
bus. When inactive, a read operation occurs and the con-
tents of the memory cells referenced by the address bus
reflect on the data out bus.
Reset—RST[A|B]
The reset pin forces the data output bus latches to zero syn-
chronously. This does not affect the memory cells of the
RAM and does not disturb a write operation on the other
port.
Address Bus—ADDR[A|B]<#:0>
The address bus selects the memory cells for read or write.
The width of the port determines the required width of this
bus as shown in Table 15.
Data In Bus—DI[A|B]<#:0>
The data in bus provides the new data value to be written
into the RAM. This bus and the port have the same width, as
shown in Table 15.
Data Output Bus—DO[A|B]<#:0>
The data out bus reflects the contents of the memory cells
referenced by the address bus at the last active clock edge.
During a write operation, the data out bus reflects the data
in bus. The width of this bus equals the width of the port.
The allowed widths appear in Table 15.
Inverting Control Pins
The four control pins (CLK, EN, WE and RST) for each port
have independent inversion control as a configuration option.
Address Mapping
Each port accesses the same set of 4096 memory cells
using an addressing scheme dependent on the width of the
port. The physical RAM location addressed for a particular
width are described in the following formula (of interest only
when the two ports use different aspect ratios).
Start = ((ADDRport +1) * Widthport) –1
End = ADDRport * Widthport
Table 16 shows low order address mapping for each port
width.
Creating Larger RAM Structures
The block SelectRAM+ columns have specialized routing to
allow cascading blocks together with minimal routing
delays. This achieves wider or deeper RAM structures with
a smaller timing penalty than when using normal routing
channels.
Location Constraints
Block SelectRAM+ instances can have LOC properties
attached to them to constrain the placement. The block
SelectRAM+ placement locations are separate from the
CLB location naming convention, allowing the LOC proper-
ties to transfer easily from array to array.
The LOC properties use the following form.
LOC = RAMB4_R#C#
RAMB4_R0C0 is the upper left RAMB4 location on the
device.
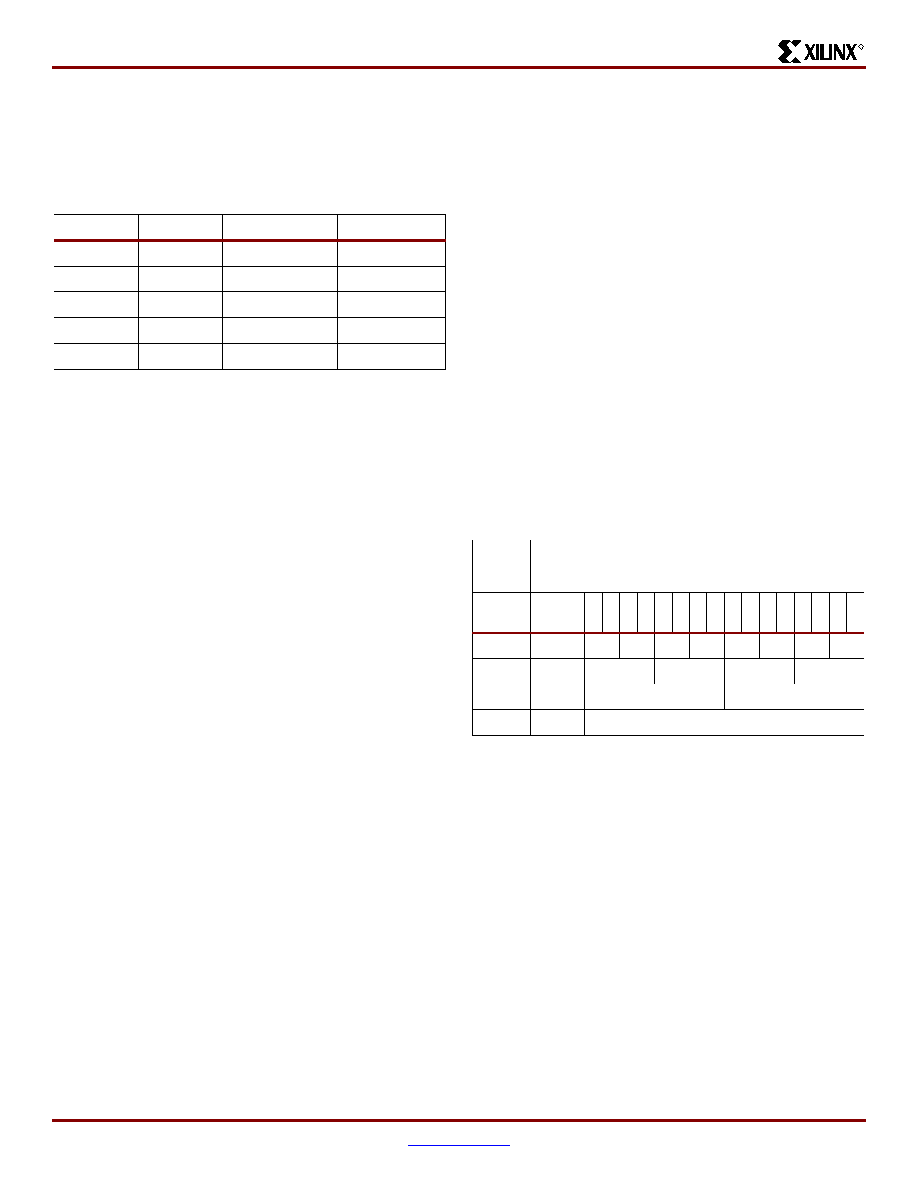
Table 15:
Block SelectRAM+ Port Aspect Ratios
Width
Depth
ADDR Bus
Data Bus
1
4096
ADDR<11:0>
DATA<0>
2
2048
ADDR<10:0>
DATA<1:0>
4
1024
ADDR<9:0>
DATA<3:0>
8
512
ADDR<8:0>
DATA<7:0>
16
256
ADDR<7:0>
DATA<15:0>
Table 16:
Port Address Mapping
Port
Width
Port
Addresses
1
4095...
1
5
1
4
1
3
1
2
1
0
9
0
8
0
7
0
6
0
5
0
4
0
3
0
2
0
1
0
2
2047...
07
06
05
04
03
02
01
00
4
1023...
03
02
01
00
8
511...
01
00
16
255...
00
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| BR93L86RFVM-WTR | IC EEPROM 16KBIT 2MHZ 8MSOP |
| BR93L86RFV-WE2 | IC EEPROM 16KBIT 2MHZ 8SSOP |
| BR25L020FV-WE2 | IC EEPROM SER 2KB SPI BUS 8SSOP |
| BR25L020FVM-WTR | IC EEPROM SER 2KB SPI BUS 8MSOP |
| BR25L020FVJ-WE2 | IC EEPROM 2KBIT 5MHZ 8TSSOP |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XCV405E-6FG900C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-6FG900I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-7BG404C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-7BG404I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-7BG556C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。