- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370833 > M30240S9-XXXFP (Mitsubishi Electric Corporation) 16 Characters x 2 Lines, 5x7 Dot Matrix Character and Cursor PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | M30240S9-XXXFP |
| 廠(chǎng)商: | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| 英文描述: | 16 Characters x 2 Lines, 5x7 Dot Matrix Character and Cursor |
| 中文描述: | 單片16位CMOS微機(jī) |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 29/142頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 1637K |
| 代理商: | M30240S9-XXXFP |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)當(dāng)前第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)第121頁(yè)第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)
1-29
Mitsubishi microcomputers
M30240 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Preliminary Specifications REV. E
Specifications in this manual are tentative and subject to change
Interrupts
2.14 Interrupts
Table 1.8 and Table 1.9 show the interrupt sources and vector table addresses. When an interrupt is
received, the program is executed from the address shown by the respective interrupt vector.
The vector table addresses for the interrupts in Table 7 are fixed (interrupt vector addresses). These
interrupts are not affected by the interrupt enable flag (I flag) (non-maskable interrupts).
The vector table addresses for the interrupts in Table 8 are variable, being determined as relative to the
fixed address in the interrupt table register (INTB). These interrupts can be enabled or disabled using
the interrupt enable flag (I flag) (maskable interrupts). Sixty four vectors can be set in the interrupt table
register (INTB). Any of software interrupts 0 to 63 can be assigned to each vector. By using the INT
instruction to specify a software interrupt number, the program can be executed starting at the address
indicated by the respective vector. The BRK instruction interrupt has interrupt vectors in both the fixed
vector address and variable vector address. When the contents of FFFE4
16
through FFFE7
16
are all
“FF
16
), the program is executed from the address shown in the BRK instruction interrupt vector in the
variable vector address.
Specify the starting address of the interrupt program in the interrupt vector. Figure 1.15 shows the format
for specifying the address.
Note: Interrupts used for debugging purposes only
Figure 1.15: Format for specifying interrupt vector addresses
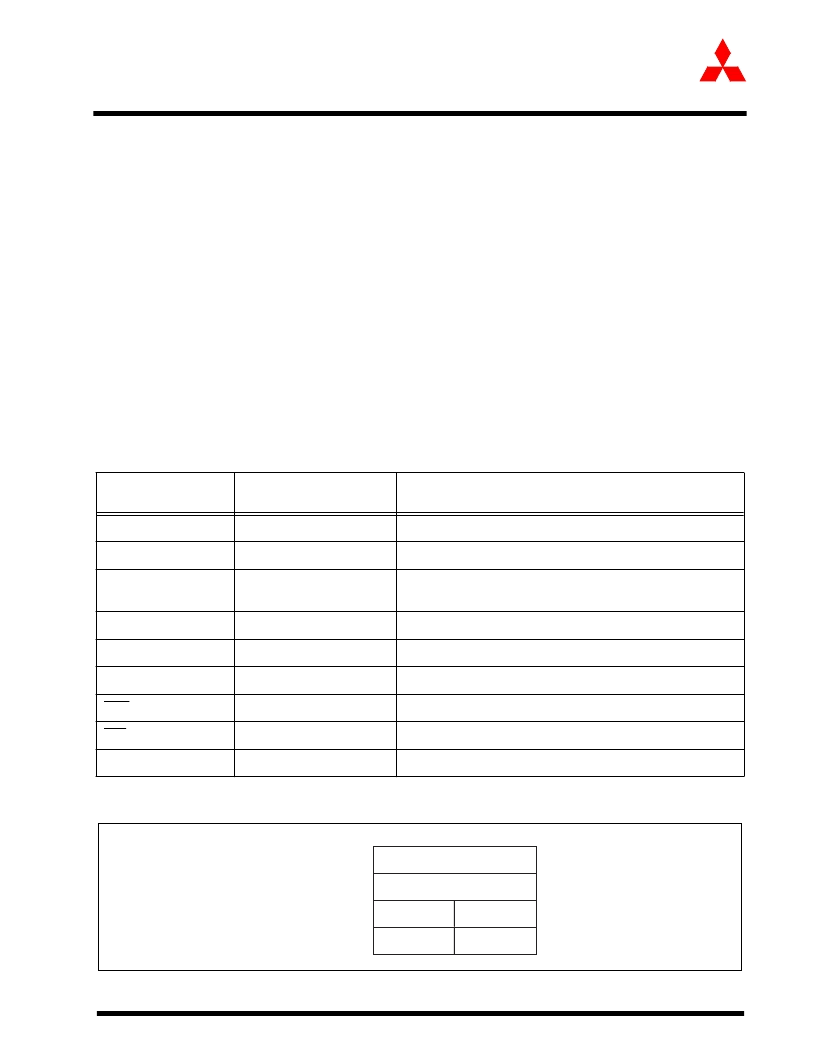
Table 1.8:
Interrupt vectors (fixed interrupt vector addresses)
Interrupt source
Vector table addresses
Address(L) to Address(H)
Remarks
Undefined instruction
FFFDC
16
to FFFDF
16
Interrupt on UND instruction
Overflow
FFFE0
16
to FFFE3
16
Interrupt on INTO instruction
BRK instruction
FFFE4
16
to FFFE7
16
If the vector is filled with FF
16
, program execution starts from
the address shown by the vector in the variable vector table
Address Match
FFFE8
16
to FFFEB
16
There is an address-matching interrupt enable bit
Single Step (Note)
FFFEC
16
to FFFEF
16
Do not use
Watchdog timer
FFFF0
16
to FFF3
16
DBC (Note)
FFFF4
16
to FFFF7
16
Do not use
NMI
FFFF8
16
to FFFFB
16
External interrupt by NMI pin
Reset
FFFFC
16
to FFFFF
16
Vector address + 3
AAAAAAAAA
Vector address + 0
0 0 0 0
Vector address + 1
Vector address + 2
LSB
MSB
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M30245M4-XXXGF | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30245F4-XXXGF | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30245M8-XXXGF | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30245F8-XXXGF | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30245F8-XXXFP | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M30240SA | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱(chēng):Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30240SA-XXXFP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱(chēng):Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30240SC | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱(chēng):Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30240SC-XXXFP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱(chēng):Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30245 | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱(chēng):Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。