- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄45237 > MC68HC05L1B (MOTOROLA INC) 8-BIT, MROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP56 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MC68HC05L1B |
| 廠商: | MOTOROLA INC |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, MROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP56 |
| 封裝: | SDIP-56 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 41/102頁 |
| 文件大小: | 632K |
| 代理商: | MC68HC05L1B |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁當(dāng)前第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁
MC68HC05L1
MOTOROLA
5-7
PROGRAMMABLE TIMER
5
5.3.2
Output Compare Register 2 (OCR2)
The 16-bit Output Compare register is made up of two 8-bit registers at location $1E (MSB) and
$1F (LSB). The contents of the Output Compare register 2 are compared with the contents of the
free-running counter continually and, if a match is found, the corresponding Output Compare Flag
(OCF2) in the Timer Status register is set and the output level (OLVL2) is transferred to pin
TCMP1. The Output Compare register 2 values and the output level bit should be changed after
each successful comparison to establish a new elapsed time-out. An interrupt can also
accompany a successful output compare provided the corresponding interrupt enable bit (OCIE)
is set. (The free-running counter is updated every four internal bus clock cycles.)
After a processor write cycle to the Output Compare register 2 containing the MSB ($1E), the
output compare function is inhibited until the LSB ($1F) is also written. The user must write both
bytes (locations) if the MSB is written rst. A write made only to the LSB ($1F) will not inhibit the
compare 2 function. The processor can write to either byte of an Output Compare register 2
without affecting the other byte. The output level (OLVL2) bit is clocked to the output level register
and hence to the TCMP2 pin whether the output compare ag 2 (OCF2) is set or clear. The
minimum time required to update the Output Compare register 2 is a function of the program
rather than the internal hardware. Because the output compare ag 2 and Output Compare
register is not dened at power-on, and not affected by reset, care must be taken when initializing
output compare functions with software. The following procedure is recommended:
–
write to Output Compare High 2 to inhibit further compares;
–
read the Timer Status register to clear OCF2 (if set);
–
write to Output Compare Low 2 to enable the output compare 2 function.
The purpose of this procedure is to prevent the OCF2 bit from being set between the time it is read
and the write to the corresponding output compare register.
All bits of the output compare register are readable and writable and are not altered by the timer
hardware or reset. If the compare function is not needed, the two bytes of the output compare
register can be used as storage locations.
5.3.3
Software Force Compare
A software force compare is required in many applications. To achieve this, bit 3 (FOLV1 for OCR1)
and bit 4 (FOLV2 for OCR2) in the Timer Control register are used. These bits always read as
‘zero’, but a write to ‘one’ causes the respective OLVL1 or OLVL2 values to be copied to the
respective output level (TCMP1 and TCMP2 pins).
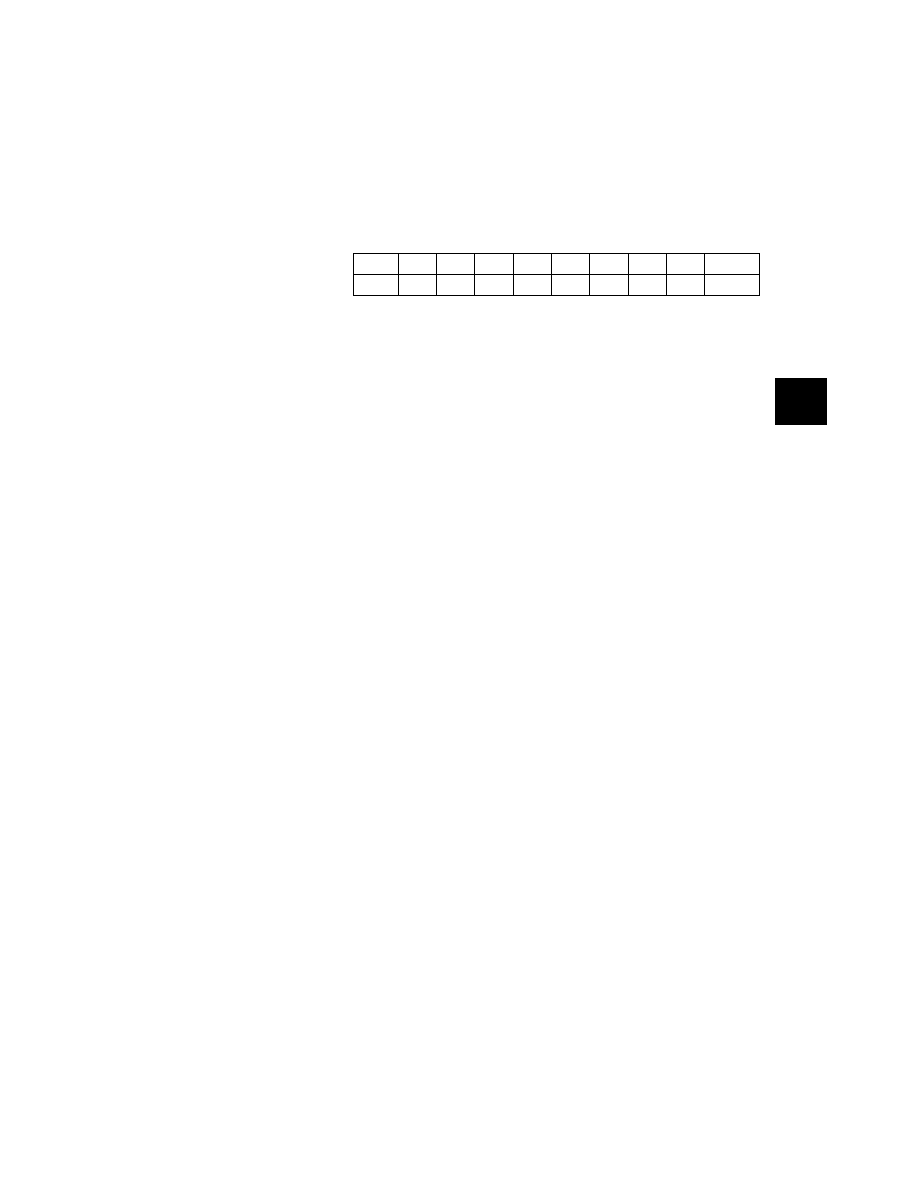
Address
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
State
on reset
Output compare high 2
$001E
unaffected
Output compare low 2
$001F
unaffected
TPG
41
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68HC705L2B | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP42 |
| MC68HC705L2CB | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP42 |
| MC68HC05L2CB | 8-BIT, MROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP42 |
| MC68HC705MC4DW | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 3 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO28 |
| MC68HC705MC4P | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 3 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP28 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68HC05L2 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:High-density complementary metal oxide semiconductor (HCMOS) microcontroller unit |
| MC68HC05L25 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Microcontrollers |
| MC68HC05L25FA | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Microcontrollers |
| MC68HC05L25PB | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Microcontrollers |
| MC68HC05L28 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:High-density complementary metal oxide semiconductor (HCMOS) microcontroller unit |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。