- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄156551 > 37C669 (SMSC Corporation) DIODE SCHOTTKY SINGLE 25V 200mW 0.5V-vf 200mA-IFM 30mA-IF 2uA-IR SOD-323 3K/REEL PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | 37C669 |
| 廠商: | SMSC Corporation |
| 英文描述: | DIODE SCHOTTKY SINGLE 25V 200mW 0.5V-vf 200mA-IFM 30mA-IF 2uA-IR SOD-323 3K/REEL |
| 中文描述: | 電腦98/99順從超級(jí)I / O軟盤(pán)控制器與紅外線支持 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 122/164頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 621K |
| 代理商: | 37C669 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)第121頁(yè)當(dāng)前第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)第143頁(yè)第144頁(yè)第145頁(yè)第146頁(yè)第147頁(yè)第148頁(yè)第149頁(yè)第150頁(yè)第151頁(yè)第152頁(yè)第153頁(yè)第154頁(yè)第155頁(yè)第156頁(yè)第157頁(yè)第158頁(yè)第159頁(yè)第160頁(yè)第161頁(yè)第162頁(yè)第163頁(yè)第164頁(yè)
60
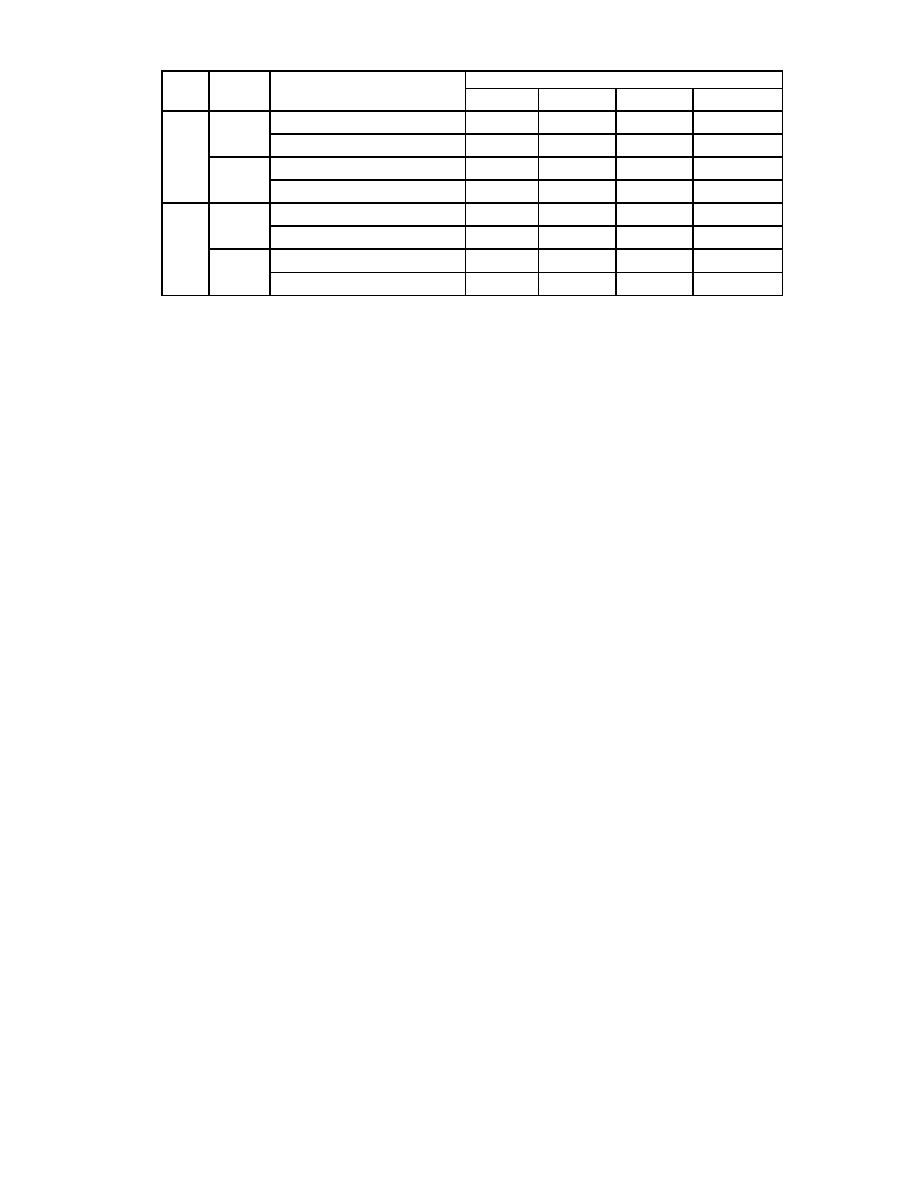
Table 24 - Result Phase Table
ID INFORMATION AT RESULT PHASE
MT
HEAD
FINAL SECTOR
TRANSFERRED TO HOST
C
H
R
N
0
Less than EOT
NC
R + 1
NC
Equal to EOT
C + 1
NC
01
NC
1
Less than EOT
NC
R + 1
NC
0
Equal to EOT
C + 1
NC
01
NC
0
Less than EOT
NC
R + 1
NC
Equal to EOT
NC
LSB
01
NC
1
Less than EOT
NC
R + 1
NC
1
Equal to EOT
C + 1
LSB
01
NC
NC: No Change, the same value as the one at the beginning of command execution.
LSB: Least Significant Bit, the LSB of H is complemented.
Write Data
After the Write Data command has been issued,
the FDC loads the head (if it is in the unloaded
state), waits the specified head load time if
unloaded (defined in the Specify command),
and begins reading ID fields. When the sector
address read from the diskette matches the
sector address specified in the command, the
FDC reads the data from the host via the FIFO
and writes it to the sector's data field.
After writing data into the current sector, the
FDC computes the CRC value and writes it into
the CRC field at the end of the sector transfer.
The Sector Number stored in "R" is incremented
by one, and the FDC continues writing to the
next data field. The FDC continues this "Multi-
Sector Write Operation".
Upon receipt of a
terminal count signal or if a FIFO over/under run
occurs while a data field is being written, then
the remainder of the data field is filled with
zeros.
The FDC reads the ID field of each sector and
checks the CRC bytes. If it detects a CRC error
in one of the ID fields, it sets the IC code in
Status
Register
0
to
"01"
(abnormal
termination), sets the DE bit of Status Register 1
to "1", and terminates the Write Data command.
The Write Data command operates in much the
same manner as the Read Data command. The
following items are the same.
Please refer to
the Read Data Command for details:
! Transfer Capacity
! EN (End of Cylinder) bit
! ND (No Data) bit
! Head Load, Unload Time Interval
! ID information when the host terminates the
command
! Definition of DTL when N = 0 and when N
does not = 0
Write Deleted Data
This command is almost the same as the Write
Data command except that a Deleted Data
Address Mark is written at the beginning of the
Data Field instead of the normal Data Address
Mark. This command is typically used to mark
a bad sector containing an error on the floppy
disk.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 37C672 | ENHANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH FAST IR |
| 37C67X | ENHANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH FAST IR |
| 37C957FR | ULTRA I/O CONTROLLER FOR PORTABLE APPLICATIONS |
| 37FMA1-ABW31N | SPECIAL SWITCH-PIEZO SWITCH, SPST, MOMENTARY, 0.2A, 24VDC, PANEL MOUNT-THREADED |
| 37FML1-BEW31N | SPECIAL SWITCH-PIEZO SWITCH, SPST, MOMENTARY, 0.2A, 24VDC, PANEL MOUNT-THREADED |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 37C672 | 制造商:SMSC 制造商全稱:SMSC 功能描述:ENHANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH FAST IR |
| 37C67X | 制造商:SMSC 制造商全稱:SMSC 功能描述:ENHANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH FAST IR |
| 37C-6BH-5-5 | 制造商:Birtcher Products 功能描述: |
| 37C72U-185 | 制造商:White-Rodgers 功能描述: |
| 37C73U-170 | 制造商:White-Rodgers 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。