- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄369950 > PCI1620PDV Controller Miscellaneous - Datasheet Reference PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | PCI1620PDV |
| 英文描述: | Controller Miscellaneous - Datasheet Reference |
| 中文描述: | 控制器雜項(xiàng)-數(shù)據(jù)表參考 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 35/164頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 720K |
| 代理商: | PCI1620PDV |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)當(dāng)前第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)第121頁(yè)第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)第143頁(yè)第144頁(yè)第145頁(yè)第146頁(yè)第147頁(yè)第148頁(yè)第149頁(yè)第150頁(yè)第151頁(yè)第152頁(yè)第153頁(yè)第154頁(yè)第155頁(yè)第156頁(yè)第157頁(yè)第158頁(yè)第159頁(yè)第160頁(yè)第161頁(yè)第162頁(yè)第163頁(yè)第164頁(yè)
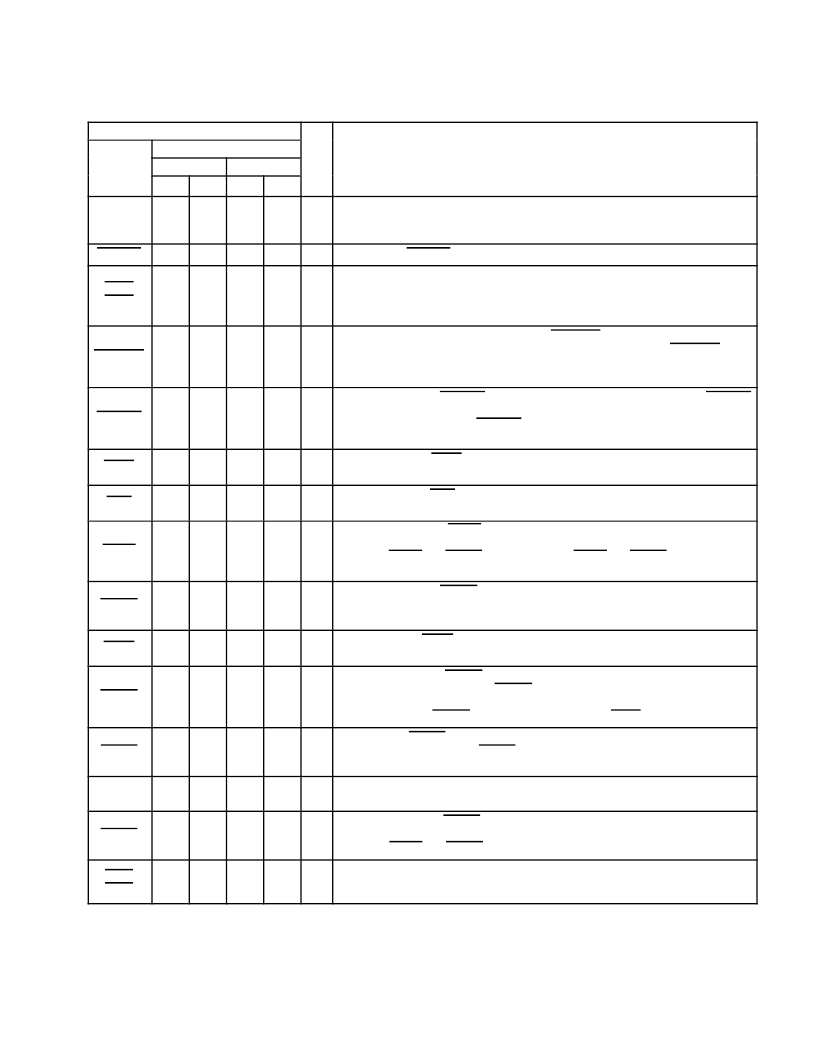
2
–
19
Table 2
–
13. CardBus PC Card Terminals (Slots A and B)
TERMINAL
NUMBER
I/O
DESCRIPTION
NAME
SLOT A
PDV
SLOT B
PDV
GHK
GHK
CAUDIO
140
H17
72
V09
I
CardBus audio. CAUDIO is a digital input signal from a PC Card to the system speaker.
The PCI1620 supports the binary audio mode and outputs a binary signal from the card to
SPKROUT.
CBLOCK
108
N14
41
N03
I/O
CardBus lock. CBLOCK is used to gain exclusive access to a target.
CCD1
CCD2
83
144
U11
G18
15
75
H05
P09
I
The card-detect terminals and the voltage-sense terminals are used together to determine
the insertion event and type of PC Card inserted (16-bit, CardBus, or UltraMedia). The
PCI1620 implements changes in the interrogation logic that handles this function. See
Section NO TAG,
PC Card Insertion/Removal and Recognition
, for more information.
CDEVSEL
113
N15
46
P03
I/O
CardBus device select. The PCI1620 asserts CDEVSEL to claim a CardBus cycle as the
target device. As a CardBus initiator on the bus, the PCI1620 monitors CDEVSEL until a
target responds. If no target responds before timeout occurs, then the PCI1620 terminates
the cycle with an initiator abort.
CFRAME
119
M15
51
R03
I/O
CardBus cycle frame. CFRAME is driven by the initiator of a CardBus bus cycle. CFRAME
is asserted to indicate that a bus transaction is beginning, and data transfers continue while
this signal is asserted. When CFRAME is deasserted, the CardBus bus transaction is in
the final data phase.
CGNT
112
P18
45
N05
O
CardBus bus grant. CGNT is driven by the PCI1620 to grant a CardBus PC Card access
to the CardBus bus after the current data transaction has been completed.
CINT
138
H19
69
V08
I
CardBus interrupt. CINT is asserted low by a CardBus PC Card to request interrupt
servicing from the host.
CIRDY
117
N18
50
P05
I/O
CardBus initiator ready. CIRDY indicates the ability of the CardBus initiator to complete the
current data phase of the transaction. A data phase is completed on a rising edge of CCLK
when both CIRDY and CTRDY are asserted. Until CIRDY and CTRDY are both sampled
asserted, wait states are inserted.
CPERR
109
R18
42
N06
I/O
CardBus parity error. CPERR reports parity errors during CardBus transactions, except
during special cycles. It is driven low by a target two clocks following the data cycle when
a parity error is detected.
CREQ
130
K17
61
R07
I
CardBus request. CREQ indicates to the arbiter that the CardBus PC Card desires use of
the CardBus bus as an initiator.
CSERR
139
H18
71
W09
I
CardBus system error. CSERR reports address parity errors and other system errors that
could lead to catastrophic results. CSERR is driven by the card synchronous to CCLK, but
deasserted by a weak pullup, and deassertion may take several CCLK periods. The
PCI1620 can report CSERR to the system by assertion of SERR on the PCI interface.
CSTOP
111
P17
44
P02
I/O
CardBus stop. CSTOP is driven by a CardBus target to request the initiator to stop the
current CardBus transaction. CSTOP is used for target disconnects, and is commonly
asserted by target devices that do not support burst data transfers.
CSTSCHG
141
H14
73
U09
I
CardBus status change. CSTSCHG alerts the system to a change in the card status, and
is used as a wake-up mechanism.
CTRDY
116
N17
49
R02
I/O
CardBus target ready. CTRDY indicates the ability of the CardBus target to complete the
current data phase of the transaction. A data phase is completed on a rising edge of CCLK,
when both CIRDY and CTRDY are asserted; until this time, wait states are inserted.
CVS1
CVS2
137
124
J14
L14
68
56
U08
P07
I/O
The card-detect terminals and the voltage-sense terminals are used together to determine
the insertion event and type of PC Card inserted (16-bit, CardBus, or UltraMedia). The
PCI1620 implements changes in the interrogation logic that handles this function.
Terminal name for slot A is preceded with A_. For example, the full name for terminals 140 and H17 are A_CAUDIO.
Terminal name for slot B is preceded with B_. For example, the full name for terminals 72 and V09 are B_CAUDIO.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PCI2050A | 32-Bit. 66MHz. 9-Master PCI-to-PCI Bridge |
| PCI2050GHK | BUS CONTROLLER |
| PCI2050PDV | BUS CONTROLLER |
| PCI9054AB50BI | Interface IC |
| PCI9036 | Telecommunication IC |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PCI-1620U | 制造商:ADVANTECH 制造商全稱(chēng):Advantech Co., Ltd. 功能描述:8-port RS-232 PCI Communication Card, with Surge Protection |
| PCI1620ZHK | 功能描述:外圍驅(qū)動(dòng)器與原件 - PCI PC Card Flash & Smart Card Cntrlr RoHS:否 制造商:PLX Technology 工作電源電壓: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:FCBGA-1156 封裝:Tray |
| PCI-1622A-BE | 制造商:Advantech Co Ltd 功能描述:8PORT RS-422/485 PCI COM CARD - Trays 制造商:Advantech Co Ltd 功能描述:8-port RS-422/485 UPCI COMM card |
| PCI-1622CU | 制造商:ADVANTECH 制造商全稱(chēng):Advantech Co., Ltd. 功能描述:8-port RS-422/485 Universal PCI Communication Card with Isolation & EFT Protection |
| PCI-1625U | 制造商:ADVANTECH 制造商全稱(chēng):Advantech Co., Ltd. 功能描述:8-port Intelligent RS-232 Universal PCI Communication Card |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。