- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄359412 > VPX3214 (Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc.) Video Pixel Decoders PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | VPX3214 |
| 廠商: | Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Video Pixel Decoders |
| 中文描述: | 視頻解碼器像素 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 7/80頁 |
| 文件大小: | 752K |
| 代理商: | VPX3214 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁當前第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁
VPX 3220 A, VPX 3216 B, VPX 3214 C
PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET
MICRONAS INTERMETALL
7
2.1.4. Digitally Controlled Clock Oscillator
The clock generation is also a part of the analog front-
end. The crystal oscillator is controlled digitally by the
control processor; the clock frequency can be adjusted
within
±
150 ppm if the recommended crystal is used.
2.1.5. Analog-to-Digital Converters
Two ADCs are provided to digitize the input signals.
Each converter runs with 20.25 MHz and has 8-bit reso-
lution. An integrated bandgap circuit generates the re-
quired reference voltages for the converters. The two
ADCs are of a 2-stage subranging type.
2.2. Color Decoder
In this block, the entire luma/chroma separation and
multistandard color demodulation is carried out. The col-
or demodulation uses an asynchronous clock, thus al-
lowing a unified architecture for all color standards.
Both luma and chroma are processed to an orthogonal
sampling raster. Luma and chroma delays are matched.
The total delay of the decoder is adjustable by a FIFO
memory. Therefore, even when the display processing
delay is included, a processing delay of exactly 64
μ
sec
can be achieved.
The color decoder output is YC
r
C
b
in a 4:2:2 format.
2.2.1. IF-Compensation
With off-air or mistuned reception, any attenuation at
higher frequencies or asymmetry around the color sub-
carrier is compensated. Three different settings of the
IF-compensation are possible:
– flat (no compensation)
– 6 dB/octave
– 12 dB/octave
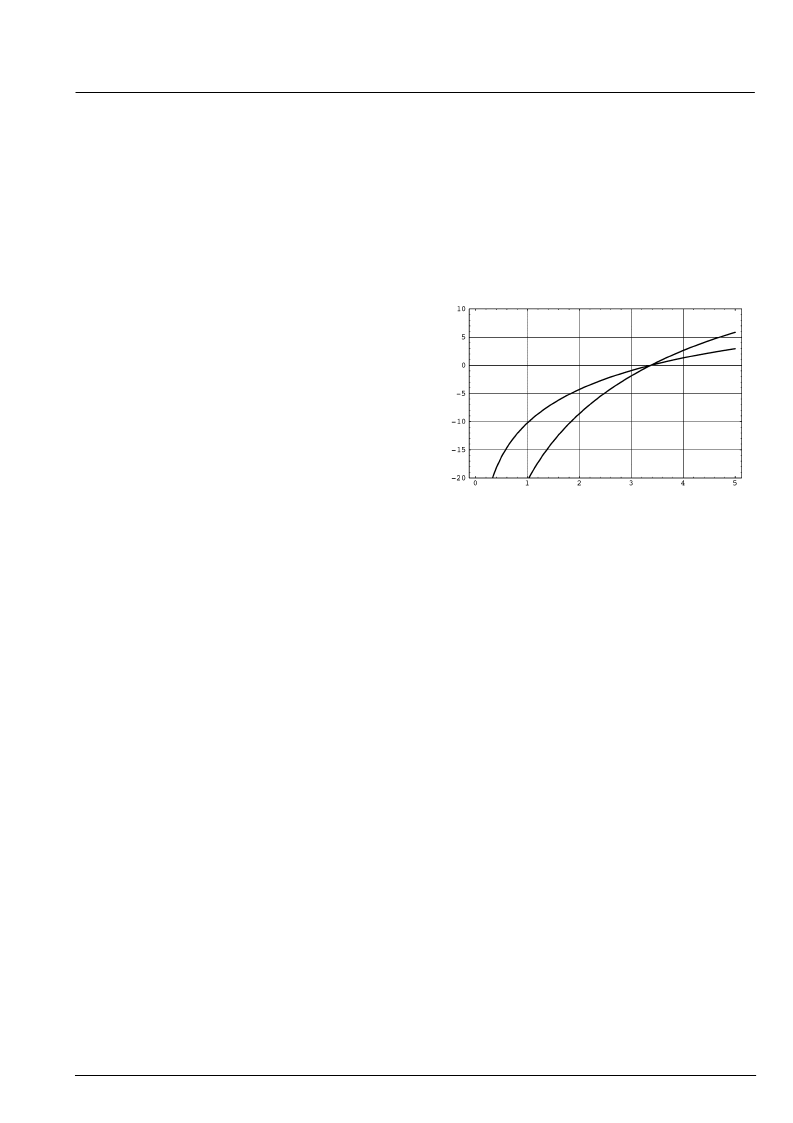
Fig. 2–3:
Frequency response of chroma IF-com-
pensation
2.2.2. Demodulator
The entire signal (which might still contain luma) is now
quadrature-mixed to the baseband. The mixing frequen-
cy is equal to the subcarrier for PAL and NTSC, thus
achieving the chroma demodulation. For SECAM, the
mixing frequency is 4.286 MHz giving the quadrature
baseband components of the FM modulated chroma.
After the mixer, a lowpass filter selects the chroma com-
ponents; a downsampling stage converts the color dif-
ference signals to a multiplexed half-rate data stream.
The subcarrier frequency in the demodulator is gener-
ated by direct digital synthesis; therefore, substandards
such as PAL 3.58 or NTSC 4.43 can also be demodu-
lated.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| VPX3214C | Video Pixel Decoders |
| VPX3224D | Video Pixel Decoders |
| VPX3224E | Video Pixel Decoders |
| VPX322XE | Video Pixel Decoders |
| VQ1000J | N-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET Transistor(最小漏源擊穿電壓60V,夾斷電流0.225A的N溝道增強型MOSFET晶體管) |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| VPX3214C | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Video Pixel Decoders |
| VPX3214C(PLCC44) | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Color Decoder Circuit |
| VPX3214C(QFP44) | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Color Decoder Circuit |
| VPX3216B | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Video Pixel Decoders |
| VPX3216B(PLCC44) | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Color Decoder Circuit |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。