- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄378045 > PCI1410GHK (Texas Instruments, Inc.) PC CARD CONTROLLERS PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | PCI1410GHK |
| 廠商: | Texas Instruments, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | PC CARD CONTROLLERS |
| 中文描述: | PC卡控制器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 58/145頁 |
| 文件大小: | 606K |
| 代理商: | PCI1410GHK |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁當(dāng)前第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁
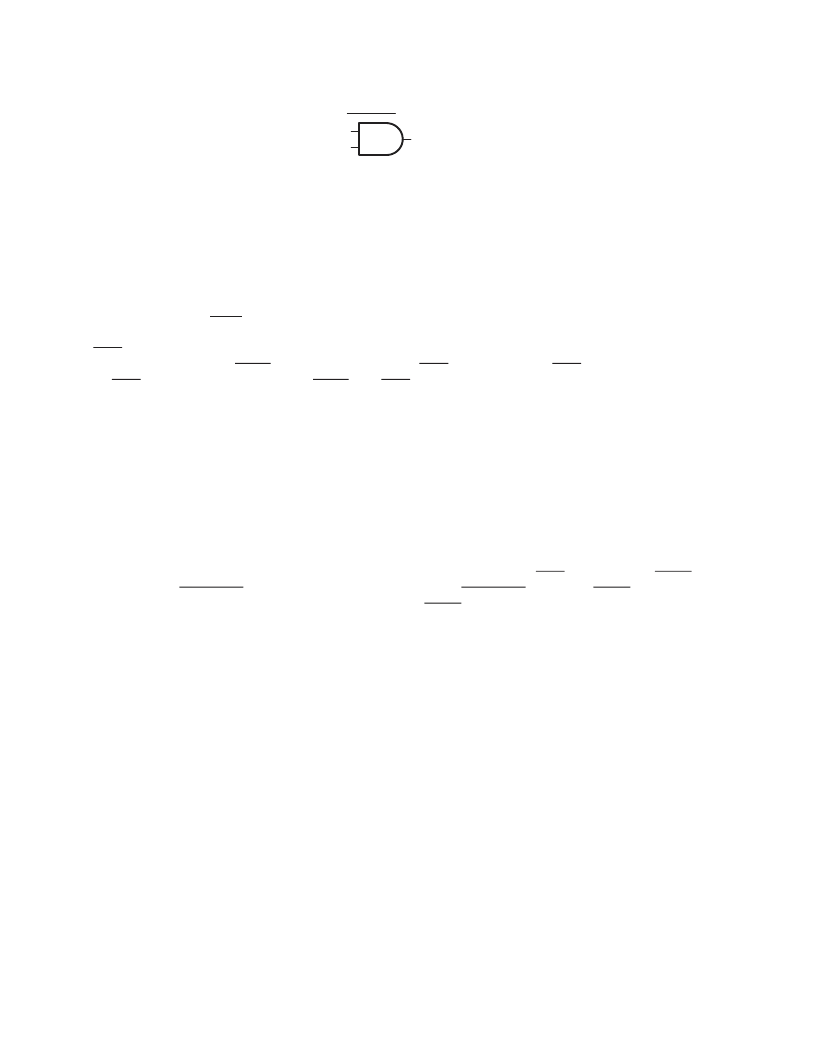
3–24
Status Bit
Event Output
Event Input
Enable Bit
Figure 3–20. Block Diagram of a Status/Enable Cell
The status and enable bits generate an event that allows the ACPI driver to call a control method associated with the
pending status bit. The control method can then control the hardware by manipulating the hardware control bits or
by investigating child status bits and calling their respective control methods. A hierarchical implementation would
be somewhat limiting, however, as upstream devices would have to remain in some level of power state to report
events.
For more information of ACPI, see the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification.
3.8.10 Master List of PME Context Bits and Global Reset Only Bits
If the PME enable bit (bit 8) of the power management control/status register (PCI offset A4h, see Section 4.40) is
asserted, then the assertion of PRST will not clear the following PME context bits. If the PME enable bit is not asserted,
then the PME context bits are cleared with PRST. The PME context bits are:
Bridge control register (PCI offset 3Eh, see Section 4.25): bit 6
Power management capabilities register (PCI offset A2h, see Section 4.39): bit 15
Power management control/status register (PCI offset A4h, see Section 4.40): bits 15, 8
ExCA power control register (ExCA offset 802h, see Section 5.3): bits 4, 3, 1, 0
ExCA interrupt and general control (ExCA offset 803h, see Section 5.4): bits 6, 5
ExCA card status-change-interrupt configuration register (ExCA offset 805h, see Section 5.6): bits 3–0
CardBus socket event register (CardBus offset 00h, see Section 6.1): bits 3–0
CardBus socket mask register (CardBus offset 04h, see Section 6.2): bits 3–0
CardBus socket present state register (CardBus offset 08h, see Section 6.3): bits 13–10, 7, 5–0
CardBus socket control register (CardBus offset 10h, see Section 6.5): bits 6–4, 2–0
Global reset will place all registers in their default state regardless of the state of the PME enable bit. The GRST signal
is gated only by the SUSPEND signal. This means that assertion of SUSPEND blocks the GRST signal internally,
thus preserving all register contents. The registers cleared by GRST are:
Subsystem vendor ID (PCI offset 40h, see Section 4.26): bits 15–0
Subsystem ID (PCI offset 42h, see Section 4.27): bits 15–0
PC Card 16-bit legacy mode base address register (PCI offset 44h): bits 31–1
System control register (PCI offset 80h, see Section 4.29): bits 31, 30, 27, 26, 24–14, 7–0
Multifunction routing register (PCI offset 8Ch, see Section 4.30): bits 27–0
Retry status register (PCI offset 90h, see Section 4.31): bits 7, 6, 3, 1
Card control register (PCI offset 91h, see Section 4.32): bits 7–5, 2–0
Device control register (PCI offset 92h, see Section 4.33): bits 7–5, 3–0
Diagnostic register (PCI offset 93h, see Section 4.34): bits 7–0
Socket DMA register 0 (PCI offset 94h, see Section 4.35): bits 1–0
Socket DMA register 1 (PCI offset 98h, see Section 4.36): bits 15–4, 2–0
General-purpose event enable register (PCI offset AAh, see Section 4.44): bits 15, 11, 8, 4–0
General-purpose output (PCI offset AEh, see Section 4.46): bits 4–0
Serial bus data (PCI offset B0h, see Section 4.47): bits 7–0
Serial bus index (PCI offset B1h, see Section 4.48): bits 7–0
Serial bus slave address register (PCI offset B2h, see Section 4.49): bits 7–0
Serial bus control and status register (PCI offset B3h, see Section 4.50): bits 7, 2
ExCA identification and revision register (ExCA offset 00h, see Section 5.1): bits 7–0
ExCA card status change register (ExCA offset 804h, see Section 5.5): bits 3–0
ExCA global control register (ExCA offset 1Eh, see Section 5.20): bits 3–0
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PCI1510GVF | PC CARD CONTROLLERS |
| PCI1510ZVF | PC CARD CONTROLLERS |
| PCI1520I | PC CARD CONTROLLERS |
| PCI4410A | PC CARD AND OHCI CONTROLLER |
| PCI4510PDV | PC CARD AND INTEGRATED 1394A-2000 OHCI TWO PORT PHY/LINK LAYER CONTROLLER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PCI1410PGE | 功能描述:外圍驅(qū)動(dòng)器與原件 - PCI PC CARD CONTROLLER RoHS:否 制造商:PLX Technology 工作電源電壓: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:FCBGA-1156 封裝:Tray |
| PCI1410RFP | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| PCI1420 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:PC Card Controllers |
| PCI1420EVM | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:PCI CARD BUS CONTROLLER EVM KIT - Bulk |
| PCI1420GHK | 功能描述:外圍驅(qū)動(dòng)器與原件 - PCI PC CARD CONTROLLER RoHS:否 制造商:PLX Technology 工作電源電壓: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:FCBGA-1156 封裝:Tray |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。