- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄359054 > M30100 (Renesas Technology Corp.) SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | M30100 |
| 廠商: | Renesas Technology Corp. |
| 英文描述: | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| 中文描述: | 單片16位CMOS微機(jī) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 23/164頁 |
| 文件大小: | 3302K |
| 代理商: | M30100 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁當(dāng)前第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁
deveopment
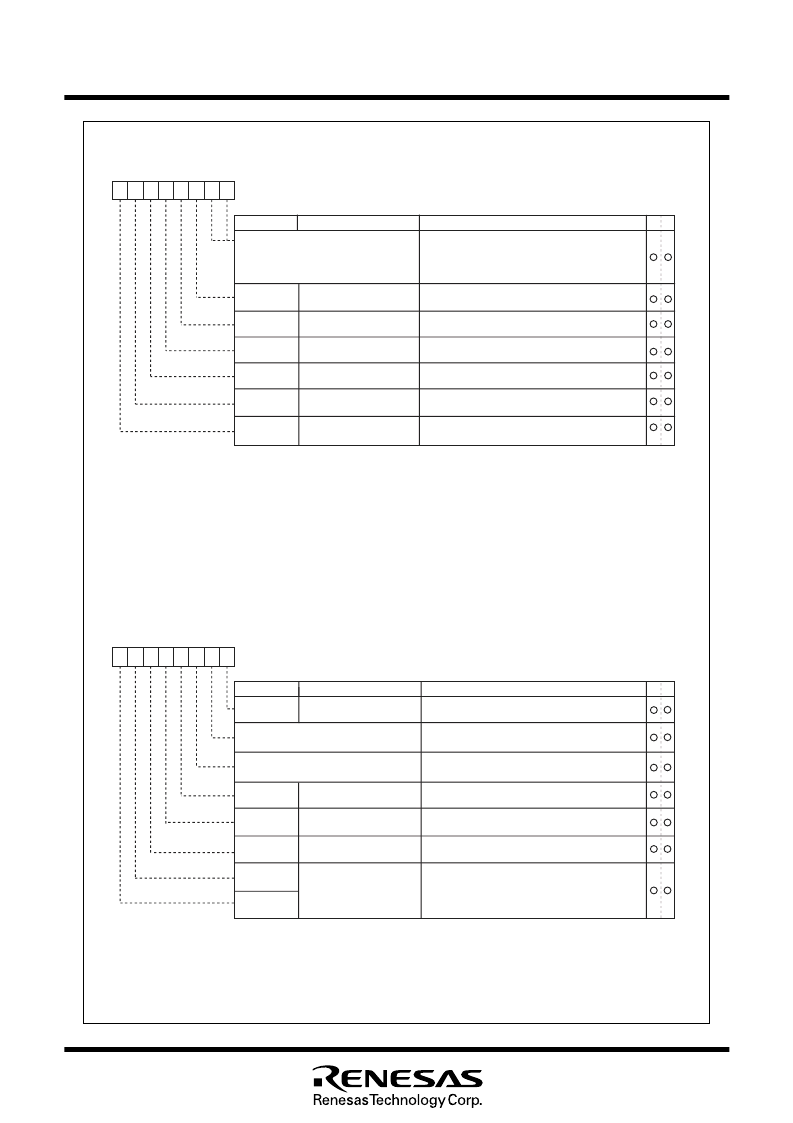
Clock Generating Circuit
Tentative Specifications REV.E1
Specifications in this manual are tentative and subject to change.
Mitsubishi microcomputers
M30100/M30102 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
22
System clock control register 0 (Note 1)
Symbol
CM0
Address
0006
16
When reset
48
16
Bit name
Function
Bit symbol
b7
b6
b5
b4 b3
b2
b1
0
b0
0
CM07
CM05
CM04
CM03
CM02
CM06
Reserved bit
WAIT peripheral function
clock stop bit
X
CIN
-X
COUT
drive capacity
select bit (Note 2)
0 : Do not stop peripheral function clock in wait mode
1 : Stop peripheral function clock in wait mode (Note 8)
0 : LOW
1 : HIGH
Port X
C
select bit
0 : I/O port
1 : X
CIN
-X
COUT
generation
0 : On
1 : Off
Main clock (X
IN
-X
OUT
)
stop bit (Note 3,4,5)
Main clock division select
bit 0 (Note 7)
0 : CM16 and CM17 valid
1 : Division by 8 mode
System clock select bit
(Note 6)
0 : X
IN
, X
OUT
1 : X
CIN
, X
COUT
Note 1: Set bit 0 of the protect register (address 000A
16
) to “1” before writing to this register.
Note 2: Changes to “1” when shifting to stop mode.
Note 3: This bit is used to stop the main clock when placing the device in a low-power mode. If you want to operate with X
IN
after exiting from the stop mode, set this bit to “0”. When operating with a self-excited oscillator, set the system clock
select bit (CM07) to “1” before setting this bit to “1”.
Note 4: When inputting external clock, only clock oscillation buffer is stopped and clock input is acceptable.
Note 5: If this bit is set to “1”, X
OUT
turns “H”. The built-in feedback resistor remains being ON, so X
IN
turns pulled up to
X
OUT
(“H”) via the feedback resistor.
Note 6: Set port Xc select bit (CM04) to “1” before setting this bit to “1”. Can not write to both bits at the same time.
Note 7: This bit changes to “1” when shifting from high-speed/medium-speed mode to stop mode and at a reset. When shifting from
low-speed/low power dissipation mode to stop mode, the value before stop mode is retained.
Note 8: fc
32
is not included. Do not set to “1” when using low-speed, low power dissipation or ring oscillator mode.
System clock control register 1 (Note 1)
Symbol
CM1
Address
0007
16
When reset
20
16
Bit name
Function
Bit symbol
b7
b6
b5
b4 b3
b2
0
b1
0
b0
CM10
All clock stop control bit
(Note 4)
0 : Clock on
1 : All clocks off (stop mode)
CM15
X
IN
-X
OUT
drive capacity
select bit (Note 2)
0 : LOW
1 : HIGH
W
R
W
R
CM16
CM17
Reserved bit
Always set to
“0”
Ring oscillation stop bit
0 : Oscillation enabled
1 : Oscillation stopped (Note 5)
Main clock division
select bit 1 (Note 3)
0 1 : Division by 2 mode
1 0 : Division by 4 mode
1 1 : Division by 16 mode
b7 b6
Reserved bit
0 : Ceramic oscillation or crystal oscillation
1 : RC oscillation
X
IN
oscillation select bit
Always set to
“0”
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
Note 1: Set bit 0 of the protect register (address 000A
16
) to “1” before writing to this register.
Note 2: This bit changes to “1” when shifting from high-speed/middle-speed mode to stop mode or at reset. When shifting from
low-speed/low power dissipation mode to stop mode, the value before stop mode is retained.
Note 3: Can be selected when bit 6 of the system clock control register 0 (address 0006
16
) is “0”. If “1”, division mode is fixed at 8.
Note 4: If this bit is set to “1”, X
OUT
turns “H”, and the built-in feedback resistor is ineffective. The mode of power control cannot
be shifted to the stop mode directly from the oscillator mode.
Note 5: This bit can be set to “1” only when both the main clock switch bit (CM22) and clock monitor bit (CM23) are set to “0” .
Moreover, this bit is automatically set to “0” if the main clock switch bit (CM22) is set to “1”.
Always set to
“0”
CM13
CM14
Figure 1.8.4. System clock control registers 0 and 1
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M30201T-56FP | Converter for Connecting Pod Probe M30201T-PRB to 56-pin 0.65mm-pitch QFP (for M30201 Group) |
| M30302FAPFP | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30620FCPFP | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M306N0FGTFP | Circular Connector; No. of Contacts:19; Series:; Body Material:Aluminum; Connecting Termination:Solder; Connector Shell Size:14; Circular Contact Gender:Pin; Circular Shell Style:Straight Plug; Insert Arrangement:14-19 |
| M306N0MCT | PTSE 19C 19#20 PIN PLUG 023 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M30-1000046 | 功能描述:集管和線殼 FEMALE CRIMP CONTACT 1.25MM PTCH 20K REEL RoHS:否 產(chǎn)品種類:1.0MM Rectangular Connectors 產(chǎn)品類型:Headers - Pin Strip 系列:DF50 觸點(diǎn)類型:Pin (Male) 節(jié)距:1 mm 位置/觸點(diǎn)數(shù)量:16 排數(shù):1 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 安裝角:Right 端接類型:Solder 外殼材料:Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) 觸點(diǎn)材料:Brass 觸點(diǎn)電鍍:Gold 制造商:Hirose Connector |
| M30100T3-RPD-E | 制造商:Renesas Electronics Corporation 功能描述:DEV EMULATOR POD M16C/10 SERIES - Bulk |
| M30100T-PTC | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:Converter for Connecting 32-pin 0.8mm-pitch QFP for M30100T-PRB (for M16C/10 Group M30100) |
| M30-1010046 | 功能描述:集管和線殼 1.25MM FEMALE CRIMP TIN PK OF 105 RoHS:否 產(chǎn)品種類:1.0MM Rectangular Connectors 產(chǎn)品類型:Headers - Pin Strip 系列:DF50 觸點(diǎn)類型:Pin (Male) 節(jié)距:1 mm 位置/觸點(diǎn)數(shù)量:16 排數(shù):1 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 安裝角:Right 端接類型:Solder 外殼材料:Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) 觸點(diǎn)材料:Brass 觸點(diǎn)電鍍:Gold 制造商:Hirose Connector |
| M3010102636207.32LLZZ | 制造商:3M Electronic Products Division 功能描述:QUOTE # V05-0068 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。