- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370847 > M37641M8-XXXHP (Mitsubishi Electric Corporation) SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | M37641M8-XXXHP |
| 廠商: | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| 英文描述: | SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| 中文描述: | 單芯片8位CMOS微機(jī) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 107/149頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1997K |
| 代理商: | M37641M8-XXXHP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁當(dāng)前第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁
107
7641 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
PRELIMINARY
Notice: This is not a final specification.
change.
Some parametric limits are subject to
Software Commands
Table 26 lists the software commands.
After setting the CPU Rewrite Mode Select Bit to
“
1
”
, write a soft-
ware command to specify an erase or program operation.
Each software command is explained below.
G
Read Array Command (FF
16
)
The read array mode is entered by writing the command code
“
FF
16
”
in the first bus cycle. When an address to be read is input in
one of the bus cycles that follow, the contents of the specified ad-
dress are read out at the data bus (DB
0
to DB
7
).
The read array mode is retained intact until another command is
written.
G
Read Status Register Command (70
16
)
When the command code
“
70
16
”
is written in the first bus cycle,
the contents of the status register are read out at the data bus
(DB
0
to DB
7
) by a read in the second bus cycle.
The status register is explained in the next section.
G
Clear Status Register Command (50
16
)
This command is used to clear the bits SR4 and SR5 of the status
register after they have been set. These bits indicate that opera-
tion has ended in an error. To use this command, write the
command code
“
50
16
”
in the first bus cycle.
G
Program Command (40
16
)
Program operation starts when the command code
“
40
16
”
is writ-
ten in the first bus cycle. Then, if the address and data to program
are written in the 2nd bus cycle, program operation (data program-
ming and verification) will start.
Whether the write operation is completed can be confirmed by
reading the status register or the RY/BY Status Flag. When the
program starts, the read status register mode is entered automati-
cally and the contents of the status register is read at the data bus
(DB
0
to DB
7
). The status register bit 7 (SR7) is set to
“
0
”
at the
Table 26 List of software commands (CPU rewrite mode)
same time the write operation starts and is returned to
“
1
”
upon
completion of the write operation. In this case, the read status reg-
ister mode remains active until the next command is written.
The RY/BY Status Flag is
“
0
”
during write operation and
“
1
”
when
the write operation is completed as is the status register bit 7.
At program end, program results can be checked by reading the
status register.
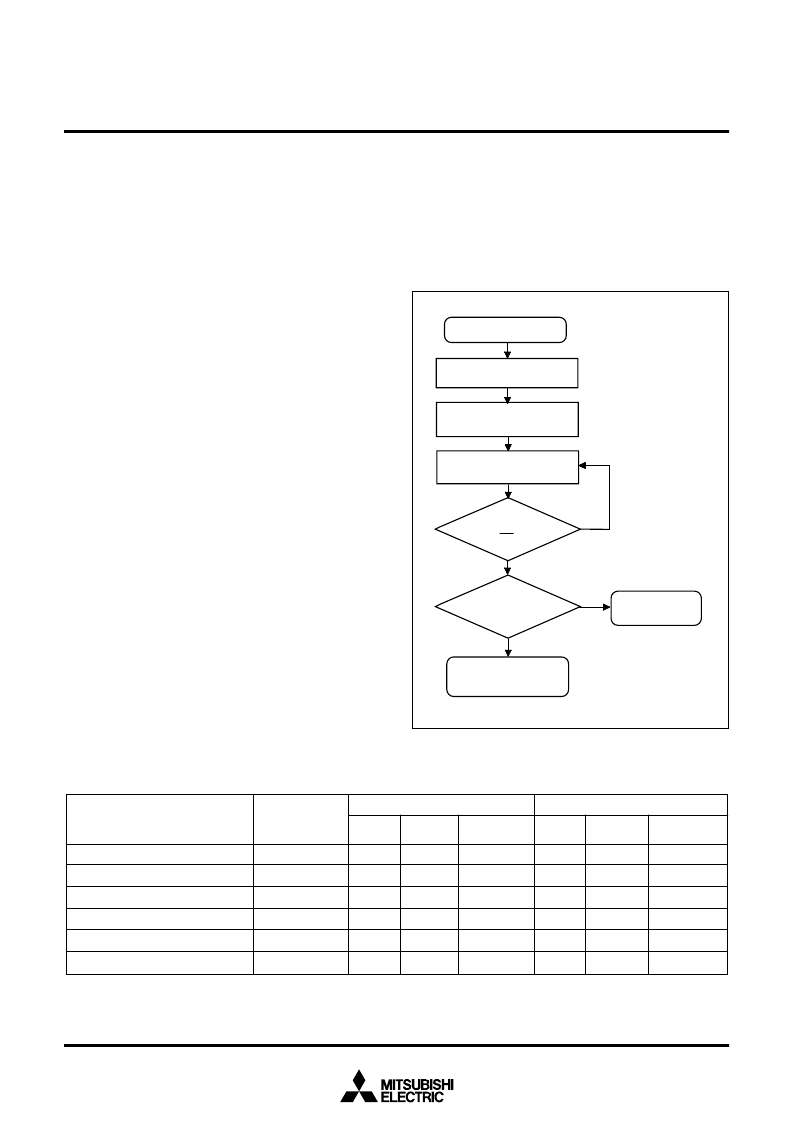
Fig. 91 Program flowchart
Command
P
r
r
o
g
r
a
m
C
l
e
a
r
s
t
a
t
u
s
r
e
g
i
s
t
e
r
R
e
e
a
d
a
r
r
a
y
R
a
d
s
t
a
t
u
s
r
e
g
i
s
t
e
r
X
X
X
F
i
r
s
t
b
u
s
c
y
c
l
e
Data
Second bus cycle
d
d
r
e
s
F
F
1
6
7
5
0
1
0
1
6
6
4
0
1
6
Write
Write
Write
Write
X
S
R
D
Read
W
r
i
t
e
E
a
s
e
a
l
l
b
l
o
c
k
s
2
0
1
6
Write
X
20
16
W
r
i
t
e
(Note 1)
WA
(Note 2)
WD
(Note 2)
Block erase
o
t
e
s
2
0
1
6
Write
D0
16
W
r
i
t
e
B
A
(Note 3)
Mode
Address
Mode
A
s
Data
B
0
t
(D
o
D
B
7
)
(
D
B
0
t
o
D
B
7
)
(Note 4)
N
1
2:
WA = Write Address, WD = Write Data
3:
BA = Block Address to be erased (Input the maximum address of each block.)
4:
X denotes a given address in the User ROM area .
:
SRD = Status Register Data
C
y
c
l
e
n
u
m
b
e
r
1
2
1
2
2
2
X
X
X
S
t
a
r
t
W
r
i
t
e
4
0
1
6
S
t
a
t
u
s
e
r
a
e
d
g
i
s
t
e
r
r
Program
completed
NO
Y
E
S
W
W
r
r
i
i
t
t
e
e
a
d
d
a
d
t
a
r
e
s
s
SR4 = 0
Program
error
NO
YES
SR7 = 1
or
RY/BY = 1
W
r
i
t
e
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M37702M2-127FP | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37702S1AFP | Single Chip 16 Bits CMOS Microcomputer(16位單片機(jī)) |
| M37702S1BFP | Single Chip 16 Bits CMOS Microcomputer(16位單片機(jī)) |
| M37702M2A | Single Chip 16 Bits CMOS Microcomputer(16位單片機(jī)) |
| M37702M2B | Single Chip 16 Bits CMOS Microcomputer(16位單片機(jī)) |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M376420RS | 制造商:OKI 功能描述:3764-20 NOTES |
| M3764-20RS | 制造商:OKI 功能描述:3764-20 NOTES 制造商: 功能描述:Dynamic RAM, Page Mode, 64K x 1, 16 Pin, Plastic, DIP 制造商:OK International 功能描述:Dynamic RAM, Page Mode, 64K x 1, 16 Pin, Plastic, DIP |
| M3-7643A-S | 制造商:Harris Corporation 功能描述: |
| M37643F8E8-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37643F8M8-XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。