- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383644 > MT90500 (Mitel Networks Corporation) Multi-Channel ATM AAL1 SAR(多通道 ATM AAL1分段及重組設備(基于通訊總線的系統(tǒng)與ATM網(wǎng)絡的接口)) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MT90500 |
| 廠商: | Mitel Networks Corporation |
| 英文描述: | Multi-Channel ATM AAL1 SAR(多通道 ATM AAL1分段及重組設備(基于通訊總線的系統(tǒng)與ATM網(wǎng)絡的接口)) |
| 中文描述: | 多通道自動柜員機AAL1特區(qū)(多通道自動柜員機AAL1分段及重組設備(基于通訊總線的系統(tǒng)與空中交通管理網(wǎng)絡的接口)) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 60/159頁 |
| 文件大小: | 514K |
| 代理商: | MT90500 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁當前第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁
MT90500
60
4.4.2.3
Receive Overruns and Underruns
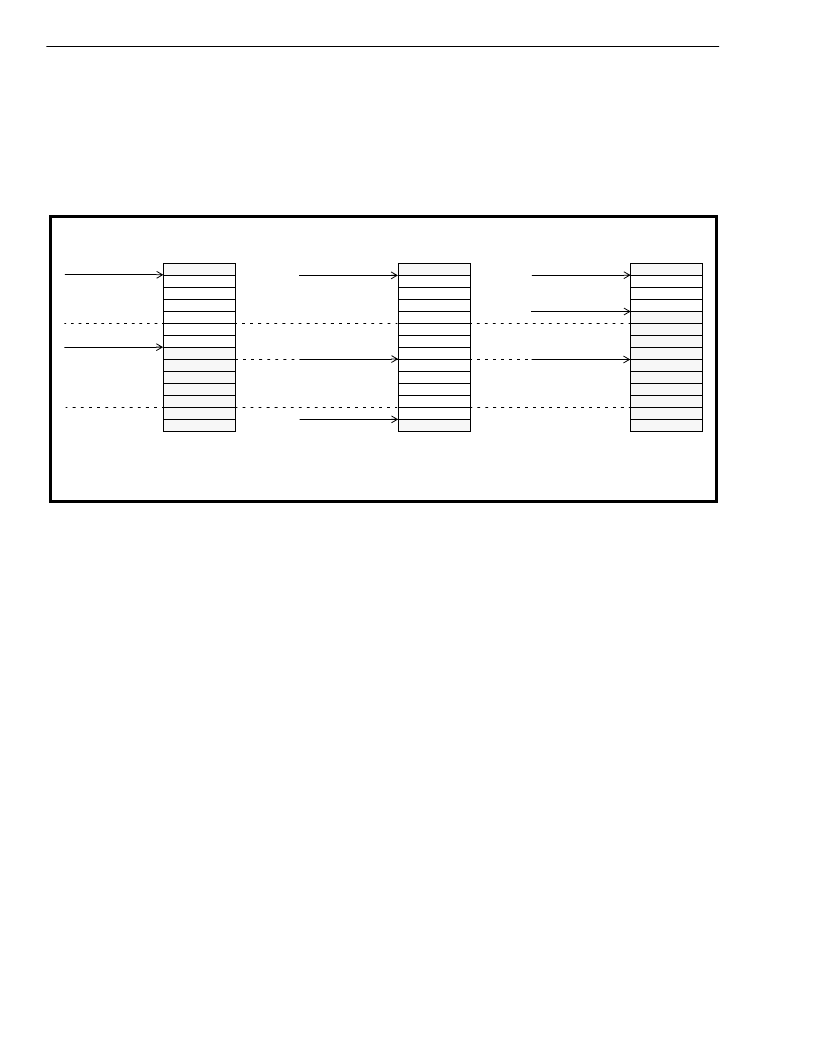
The “First Entry” and “Last Entry” fields in the RX_SAR Control Structure point to the first and last RX Circular
Buffer Base Address pointers in the RX_SAR Control Structure. The “Minimum Lead”, “Maximum Lead”, and
“Average Lead” entries define the window within the circular buffer within which cell data can be received
without generating an underrun or overrun condition. This window is defined relative to the TDM Circular Buffer
Read Pointer, as described in Figure 23. Whenever data from a newly received cell is to be written to the
Receive Circular Buffers, the location of the RX_SAR Write Pointer is checked against the Minimum and
Maximum Lead Pointers.
When a new cell is received, the hardware checks for the location of the RX_SAR Write Pointer, which
indicates where the new cell should be written within the associated Receive Circular Buffer(s). The VALID
bytes shown in the figure above indicate bytes which have been written by the RX_SAR and have yet to be
read by the External Memory to TDM Data Output Process. Consequently, INVALID bytes represent those that
have already been read or, in the case of start-up, have never been written. If the pointer falls within the window
defined by the Min. Lead and Max. Lead parameters, the new data is written immediately following the old data.
If the RX_SAR Write Pointer falls after the Maximum Lead Pointer, an overrun condition is detected, and the
new data is written starting at the location of the Average Lead Pointer. (Some addresses containing previously
received, unread data bytes are overwritten.) If the RX_SAR Write Pointer falls before of the Minimum Lead
Pointer, an underrun condition is detected, and the new data is written starting at the location of the Average
Lead Pointer. (Some addresses containing already-read data bytes are “skipped” and left unwritten.) Figure 23
depicts the Write Pointer to Read Pointer comparison that occurs at cell receive time.
The External Memory to TDM Data Output Process (Section 4.1.4) has its own TDM Read Underrun Error
indication (see register 6000h) which works in parallel to the mechanism described above. The ninth bit of the
external memory byte is not used for parity, but is used to indicate whether each TDM byte has been previously
transferred to the TDM bus. When the External Memory to TDM Data Output Process reads a byte which has
already been transferred (has the ninth bit set), an underrun condition is flagged, if enabled by that TDM
channel’s entry in the External Memory to Internal Memory Control Structure. Since this TDM Read Underrun
Error functions as each byte is read (and not just when a cell arrives, as the RX_SAR errors do) it is useful to
indicate dropped VCs (no cells), and excessive CDV (late cells).
Data bytes which have been read out to the TDM bus by the External Memory to TDM Data Output Process are
handled according to the programming of the External Memory to Internal Memory Control Structure.
Depending on the value of the write-back disable bit for each individual TDM channel, bytes read out to the
TDM bus will either be replaced by silence (FFh) or left unchanged. This has the effect that in the event of an
underrun, either silence (FFh) will be read out of the “skipped” area, or the old data in the “skipped” area will be
repeated on the TDM bus.
RECEIVE BUFFER
TDM CIRC. BUFFER
READ POINTER
Min. Lead
Max. Lead
Figure 23 - Overrun and Underrun Situations
WRITE POINTER
RECEIVE BUFFER
Max. Lead
WRITE POINTER
(OLD)
Normal
Overrun
Underrun
RECEIVE BUFFER
Avg. Lead
INVALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
Avg. Lead
WRITE POINTER
(NEW)
INVALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
VALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
INVALID BYTE
Min. Lead
WRITE POINTER
(NEW)
WRITE POINTER
(OLD)
Min. Lead
Max. Lead
RX_SAR
RX_SAR
RX_SAR
RX_SAR
RX_SAR
TDM CIRC. BUFFER
READ POINTER
TDM CIRC. BUFFER
READ POINTER
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MT90500 | Multi-Channel ATM AAL1 SAR |
| MT90500AL | Multi-Channel ATM AAL1 SAR |
| MT90502 | Multi-Channel AAL2 SAR(多通道 ATM AAL2分段及重組設備(基于通訊總線的系統(tǒng)與ATM網(wǎng)絡的接口)) |
| MT90732AP | Ultraframer DS3/E3/DS2/E2/DS1/E1/DS0 |
| MT90732 | Ultraframer DS3/E3/DS2/E2/DS1/E1/DS0 |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MT90500AL | 制造商:MITEL 制造商全稱:Mitel Networks Corporation 功能描述:Multi-Channel ATM AAL1 SAR |
| MT90500AL-ENG1 | 制造商:Mitel Networks Corporation 功能描述: |
| MT90502 | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Multi-Channel AAL2 SAR |
| MT90502_06 | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Multi-Channel AAL2 SAR |
| MT90502AG | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述: 制造商:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。