- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄18714 > AD9852/PCBZ (Analog Devices Inc)BOARD EVAL FOR AD9852 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | AD9852/PCBZ |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 11/52頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | BOARD EVAL FOR AD9852 |
| 設(shè)計(jì)資源: | AD9852 Eval Brd BOM AD9852 Schematic |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 1 |
| 系列: | AgileRF™ |
| 類型: | 合成器 |
| 適用于相關(guān)產(chǎn)品: | AD9852 |
| 相關(guān)產(chǎn)品: | AD9852ASVZ-ND - IC DDS SYNTHESIZER CMOS 80-TQFP AD9852ASTZ-ND - IC DDS SYNTHESIZER CMOS 80-LQFP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁當(dāng)前第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁
AD9852
Rev. E | Page 19 of 52
Table 7. Function Availability vs. Mode of Operation
Function
Single-Tone Mode
FSK Mode
Ramped FSK Mode
Chirp Mode
BPSK Mode
Phase Adjust 1
●
Phase Adjust 2
●
Single-Pin FSK/BPSK or HOLD
●
Single-Pin Output Shaped Keying
●
Phase Offset or Modulation
●
Amplitude Control or Modulation
●
Inverse Sinc Filter
●
Frequency Tuning Word 1
●
Frequency Tuning Word 2
●
Automatic Frequency Sweep
●
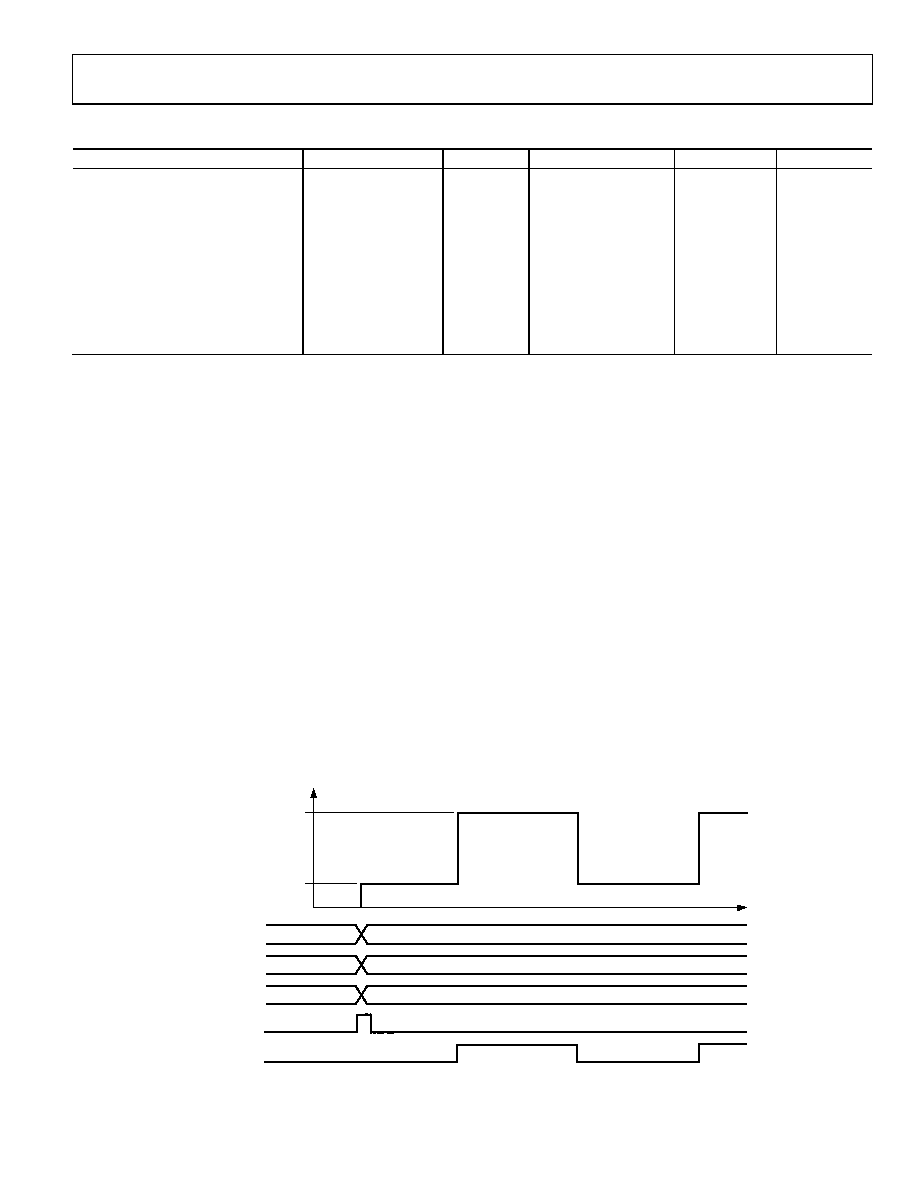
UNRAMPED FSK (MODE 001)
When this mode is selected, the output frequency of the DDS is
a function of the values loaded into Frequency Tuning Word
Register 1 and Frequency Tuning Word Register 2 and the logic
level of Pin 29 (FSK/BPSK/HOLD). A logic low on Pin 29
chooses F1 (Frequency Tuning Word 1, Parallel Address 4 hex
to Parallel Address 9 hex), and a logic high chooses F2
(Frequency Tuning Word 2, Parallel Register Address A hex to
Parallel Register Address F hex). Changes in frequency are
phase continuous and are internally coincident with the FSK
data pin (Pin 29); however, there is deterministic pipeline delay
between the FSK data signal and the DAC output (see Table 1).
The unramped FSK mode (see Figure 33) is representative
of traditional FSK, radio teletype (RTTY), or teletype (TTY)
transmission of digital data. FSK is a very reliable means of
digital communication; however, it makes inefficient use of
the bandwidth in the RF spectrum. Ramped FSK, shown in
Figure 34, is a method of conserving the bandwidth.
RAMPED FSK (MODE 010)
In this method of FSK, changes from F1 to F2 are not
instantaneous, but are accomplished in a frequency sweep or
ramped fashion. The ramped notation implies the sweep is
linear. Although linear sweeping, or frequency ramping, is
easily and automatically accomplished, it is only one of many
possibilities. Other frequency transition schemes can be
implemented by changing the ramp rate and ramp step size at
any time during operation.
Frequency ramping, whether linear or nonlinear, necessitates
that many intermediate frequencies between F1 and F2 are
output in addition to the primary F1 and F2 frequencies.
time characteristics of a linear ramped FSK signal.
In ramped FSK mode, the delta frequency word (DFW) is
required to be programmed as a positive twos complement
value. Another requirement is that the lowest frequency (F1) be
programmed in the Frequency Tuning Word 1 registers.
F1
F2
0
FREQUENCY
MODE
TW1
TW2
FSK DATA (PIN 29)
001 (FSK NO RAMP)
F1
F2
000 (DEFAULT)
0
I/O UD CLK
00634-033
Figure 33. Unramped (Traditional) FSK Mode
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| X24-009-DK | KIT DEV 2.4GHZ 9600BPS W/RPSMA |
| 0622022510 | TOOL INSERTION 30POS 3ROWS |
| TC70V3I32K7680 | OSCILLATOR 32.7680 KHZ 1.5V SMD |
| TC70M3I32K7680 | OSCILLATOR 32.7680 KHZ 1.8V SMD |
| TC70N3I32K7680 | OSCILLATOR 32.7680 KHZ 2.5V SMD |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| AD9853 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:Programmable Digital OPSK/16-QAM Modulator |
| AD9853-45PCB | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:Programmable Digital OPSK/16-QAM Modulator |
| AD9853-65PCB | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:Programmable Digital OPSK/16-QAM Modulator |
| AD9853AS | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述: 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| AD9854 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:CMOS 300 MHz Quadrature Complete-DDS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。