- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄375996 > GE28F128W30B90 CHIP RESISTOR PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | GE28F128W30B90 |
| 英文描述: | CHIP RESISTOR |
| 中文描述: | 的EEPROM | FLASH動畫| 8M × 16位|的CMOS | BGA封裝| 60PIN |塑料 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 22/91頁 |
| 文件大小: | 994K |
| 代理商: | GE28F128W30B90 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁當前第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁
1.8 Volt Intel
Wireless Flash Memory with 3 Volt I/O
22
Datasheet
4.3
Read Query (CFI)
This device contains a separate CFI query
database
that acts as an “on-chip datasheet.” The CFI
information within this device can be accessed by issuing the Read Query command and supplying
a specific address. The address is constructed from the base address of a partition plus a particular
offset corresponding to the desired CFI field.
Appendix B, “Common Flash Interface” on page 80
shows accessible CFI fields and their address offsets. Issuing the Read Query command to a
partition that is programming or erasing puts that partition in read query mode while the partition
continues to program or erase in the background.
4.4
Read Status Register
The device’s status register displays program and erase operation status. A partition’s status can be
read after writing the Read Status Register command to any location within the partition’s address
range. Read-status mode is the default read mode following a Program, Erase, or Lock Block
command sequence. Subsequent single reads from that partition will return its status until another
valid command is written.
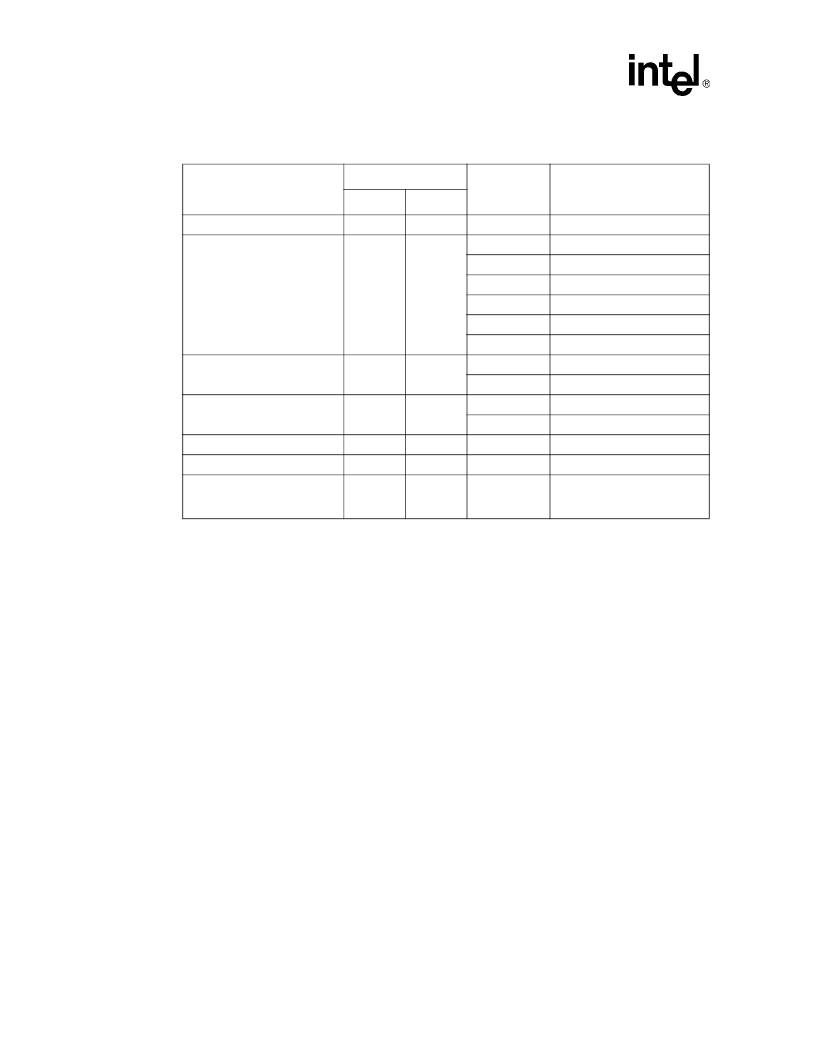
Table 7.
Device Identification Codes
Item
Address
1
Data
Description
Base
Offset
Manufacturer ID
Partition
00h
0089h
Device ID
Partition
01h
8852h
32-Mbit TPD
8853h
32-Mbit BPD
8854h
64-Mbit TPD
8855h
64-Mbit BPD
8856h
128-Mbit TPD
8857h
128-Mbit BPD
Block Lock Status
(2)
Block
02h
D0 = 0
Block is unlocked
D0 = 1
Block is locked
Block Lock-Down Status
(2)
Block
02h
D1 = 0
Block is not locked-down
D1 = 1
Block is locked down
Configuration Register
Partition
05h
Register Data
Protection Register Lock Status
Partition
80h
Lock Data
Protection Register
Partition
81h - 88h
Register Data
Multiple reads required to read
the entire 128-bit Protection
Register.
NOTES:
1. The address is constructed from a base address plus an offset. For example, to read the Block Lock Status
for block number 38 in a BPD, set the address to the BBA (0F8000h) plus the
offset
(02h), i.e. 0F8002h.
Then examine bit 0 of the data to determine if the block is locked.
2. See
Section 7.1.4, “Block Lock Status” on page 38
for valid lock status.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| GE28F128W30T90 | EEPROM|FLASH|8MX16|CMOS|BGA|60PIN|PLASTIC |
| GE28F640W30B70 | EEPROM|FLASH|4MX16|CMOS|BGA|56PIN|PLASTIC |
| GE28F640W30B85 | EEPROM|FLASH|4MX16|CMOS|BGA|56PIN|PLASTIC |
| GE28F640W30T70 | EEPROM|FLASH|4MX16|CMOS|BGA|56PIN|PLASTIC |
| GE28F640W30T85 | EEPROM|FLASH|4MX16|CMOS|BGA|56PIN|PLASTIC |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| GE28F128W30T90 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:EEPROM|FLASH|8MX16|CMOS|BGA|60PIN|PLASTIC |
| GE28F160B3BC70 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:3 Volt Advanced Boot Block Flash Memory |
| GE28F160B3BC80 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:3 Volt Advanced Boot Block Flash Memory |
| GE28F160B3TC70 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:3 Volt Advanced Boot Block Flash Memory |
| GE28F160B3TC80 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:3 Volt Advanced Boot Block Flash Memory |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。