- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄367625 > MFRC53001T (NXP Semiconductors N.V.) ISO-IEC 14443 A Reader IC PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MFRC53001T |
| 廠商: | NXP Semiconductors N.V. |
| 元件分類: | 通信及網(wǎng)絡(luò) |
| 英文描述: | ISO-IEC 14443 A Reader IC |
| 封裝: | MFRC53001T/0FE<SOT287-1 (SO32)|<<http://www.nxp.com/packages/SOT287-1.html<1<week 5, 2005,;MFRC53001T/0FE<SOT287-1 (SO32)|<<http://www.nxp.com/packages/SOT287-1.html<1 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 16/115頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 2590K |
| 代理商: | MFRC53001T |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁當(dāng)前第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁
MFRC530_33
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers.
NXP B.V. 2010. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet
PUBLIC
Rev. 3.3 — 6 July 2010
057433
16 of 115
NXP Semiconductors
MFRC530
ISO/IEC 14443 A Reader IC
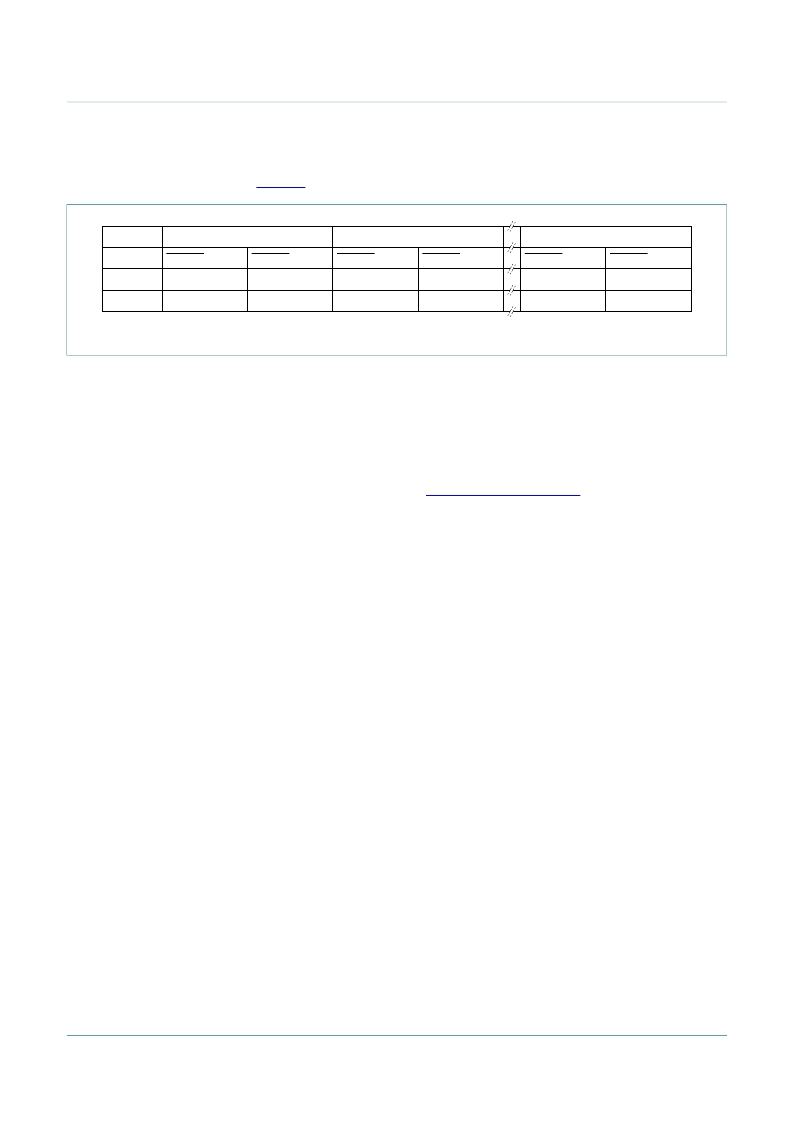
Using this format, 12 bytes of EEPROM memory are needed to store a 6-byte key. This is
shown in
Figure 7
.
Example
: The value for the key must be written to the EEPROM.
If the key was: A0h A1h A2h A3h A4h A5h then
5Ah F0h 5Ah E1h 5Ah D2h 5Ah C3h 5Ah B4h 5Ah A5h would be written.
Remark:
It is possible to load data for other key formats into the EEPROM key storage
location. However, it is not possible to validate card authentication with data which will
cause the LoadKeyE2 command (see
Section 11.6.1 on page 86
) to fail.
9.2.3.2
Storage of keys in the EEPROM
The MFRC530 reserves 384 bytes of memory in the EEPROM for the Crypto1 keys. No
memory segmentation is used to mirror the 12-byte structure of key storage. Thus, every
byte of the dedicated memory area can be the start of a key.
Example
: If the key loading cycle starts at the last byte address of an EEPROM block, (for
example, key byte 0 is stored at 12Fh), the next bytes are stored in the next EEPROM
block, for example, key byte 1 is stored at 130h, byte 2 at 131h up to byte 11 at 13Ah.
Based on the 384 bytes of memory and a single key needing 12 bytes, then up to 32
different keys can be stored in the EEPROM.
Remark:
It is not possible to load a key exceeding the EEPROM byte location 1FFh.
9.3 FIFO buffer
An 8
×
64 bit FIFO buffer is used in the MFRC530 to act as a parallel-to-parallel converter.
It buffers both the input and output data streams between the microprocessor and the
internal circuitry of the MFRC530. This makes it possible to manage data streams up to
64 bytes long without needing to take timing constraints into account.
9.3.1
Accessing the FIFO buffer
9.3.1.1
Access rules
The FIFO buffer input and output data bus is connected to the FIFOData register. Writing
to this register stores one byte in the FIFO buffer and increments the FIFO buffer write
pointer. Reading from this register shows the FIFO buffer contents stored at the FIFO
buffer read pointer and increments the FIFO buffer read pointer. The distance between the
write and read pointer can be obtained by reading the FIFOLength register.
Fig 7.
Key storage format
001aak640
0 (LSB)
Master key byte
Master key bits
EEPROM byte
address
Example
k7 k6 k5 k4 k7 k6 k5 k4
n
5Ah
k3 k2 k1 k0 k3 k2 k1 k0
n + 1
F0h
1
k7 k6 k5 k4 k7 k6 k5 k4
n + 2
5Ah
k3 k2 k1 k0 k3 k2 k1 k0
n + 3
E1h
5 (MSB)
k7 k6 k5 k4 k7 k6 k5 k4
n + 10
5Ah
k3 k2 k1 k0 k3 k2 k1 k0
n + 11
A5h
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MFRC53101T | ISO-IEC 14443 reader IC |
| MFRX85201HD | Secure contactless reader solution |
| MMBD4148 | High-speed switching diode |
| MMBD6050-V-GS08 | SWITING 70V 0.2A 3PIN SOT-23 - Tape and Reel |
| MMBD6050-V-GS18 | SWITING 70V 0.2A 3PIN SOT-23 - Tape and Reel |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MFRC53001T/0FE | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:ISO/IEC 14443 A Reader IC |
| MFRC53001T/0FE,112 | 功能描述:RFID應(yīng)答器 MIFARE HS READER RoHS:否 制造商:Murata 存儲(chǔ)容量:512 bit 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Reel |
| MFRC53001T/0FE,518 | 功能描述:RFID應(yīng)答器 IC READER 13.56MHZ RoHS:否 制造商:Murata 存儲(chǔ)容量:512 bit 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Reel |
| MFRC53001T/0FE112 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:CNTCLESS RC 3.3V ISO14443-A/B |
| MFRC531 | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Short Form Specification |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。