- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370008 > PM2329 Telecommunication IC PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | PM2329 |
| 英文描述: | Telecommunication IC |
| 中文描述: | 通信集成電路 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 70/162頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 1581K |
| 代理商: | PM2329 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)當(dāng)前第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)第121頁(yè)第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)第143頁(yè)第144頁(yè)第145頁(yè)第146頁(yè)第147頁(yè)第148頁(yè)第149頁(yè)第150頁(yè)第151頁(yè)第152頁(yè)第153頁(yè)第154頁(yè)第155頁(yè)第156頁(yè)第157頁(yè)第158頁(yè)第159頁(yè)第160頁(yè)第161頁(yè)第162頁(yè)
Proprietary and Confidential to PMC-Sierra, Inc and for its Customers
’
Internal Use
Document ID: PMC-2010146, Issue 4
73
PM2329 ClassiPI Network Classification Processor Datasheet
The PM2329 channels are implemented through segmentation of the Packet Buffer and the Results FIFO.
Channel segments may be concatenated to allow larger packet or result storage for a given channel (with
correspontingly fewer channels supported).
4.1.3 Channel Register Blocks
PM2329 registers involved in packet transfer, packet processing status and packet results are organized
into Channel Register blocks. There is one block of Channel registers for each of the 32 possible channels.
These registers reside in Global address space. Thus, every PM2329 in a cascade has them, and a write to
them by the network processor affects all devices in the cascade.
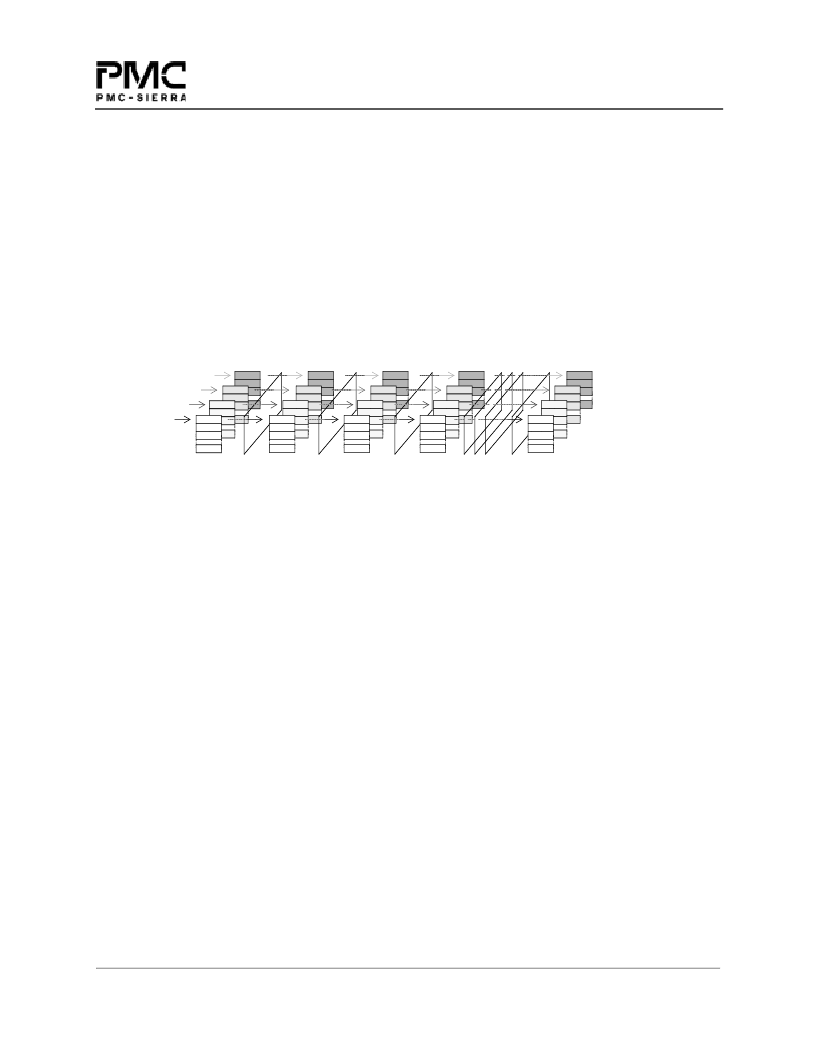
Figure 24 Channel Register Blocks
As illustrated in Figure 24, each channel
’
s register block is spread over four address regions identified by
base addresses 0 to 3. However, the specific registers of each channel have a unique offset relative to base
addresses. That is, for any given channel, the offset distinguishes the channel
’
s registers from
corresponding registers of other channels. Thus, each context on the packet processor can access a
particular channel easily, and perform its own packet processing independently. (The four base address
spaces differ in size, so a channel
’
s offset from Base 0 will differ from its offset from Base 1, or 2, or 3.)
Figure 25 and Table 18 show the complete Register Block address space.
4.1.4 Direct and Indirect Access
The registers of the PM2329 are accessed using direct addressing by directly reading or writing to these
registers. Memory locations controlled by the PM2329 (the E-RAM and PM2329 Rule Memory), however,
are accessed using Indirect Addressing. This is done by writing and reading a set of Address, Data and
Command Registers. The following registers provide indirect access to the Rule Memory:
Rule Indirect Address Register,
Rule Indirect Data Register, and
Rule Indirect Command Register.
The following registers provide indirect access to the E-RAM:
E-RAM Indirect Address Register,
E-RAM Indirect Data Register, and
E-RAM Indirect Command Register.
Base 3 addresses
Base 2 addresses
Base 1 addresses
Base 0 addresses
Regisfor
Channel
0
Regisfor
Channel
1
Regisfor
Channel
2
Regisfor
Channel
3
Regisfor
Channel
31
no offset from
base addresses
CH1
’
s offsets
from bases
CH2
’
s offsets
from bases
CH3
’
s offsets
from bases
CH31
’
s offsets
from bases
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PM239P | Analog Comparator |
| PM30RHC060 | TRANSISTOR | IGBT POWER MODULE | 3-PH BRIDGE | 600V V(BR)CES | 30A I(C) |
| PM3321-QC | DATA CROSS CONNECT|LDCC|84PIN|PLASTIC |
| PM355AJ | Voltage-Feedback Operational Amplifier |
| PM355AZ | Voltage-Feedback Operational Amplifier |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PM233-155.52M | 制造商:CONNOR-WINFIELD 制造商全稱:Connor-Winfield Corporation 功能描述:5.0x7.0mm Surface Mount LVPECL Clock Oscillator Series |
| PM2379-001 | 制造商:Delphi Corporation 功能描述:TAPE MARK WHT |
| PM238 | 制造商:PURDY 制造商全稱:PURDY 功能描述:AC Fans and Blowers |
| PM238-115-1751BT-4 | 制造商:INTERFAN 功能描述:Fan, AC, 115V, 172x150x51mm, Obround, 238CFM, 3100RPM, 55dBA, Terminal Block |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。