- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄295065 > AM79C965KCW (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC) 3 CHANNEL(S), LOCAL AREA NETWORK CONTROLLER, PQFP16 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | AM79C965KCW |
| 廠商: | ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 3 CHANNEL(S), LOCAL AREA NETWORK CONTROLLER, PQFP16 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, QFP-160 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 80/220頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1197K |
| 代理商: | AM79C965KCW |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁當(dāng)前第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁第193頁第194頁第195頁第196頁第197頁第198頁第199頁第200頁第201頁第202頁第203頁第204頁第205頁第206頁第207頁第208頁第209頁第210頁第211頁第212頁第213頁第214頁第215頁第216頁第217頁第218頁第219頁第220頁
AMD
P R E L I M I N A R Y
170
Am79C965
18219B-44
47
1
0
RECEIVED MESSAGE
DESTINATION ADDRESS
1
CRC
GEN
SEL
31
26
0
MUX
MATCH
PACKET ACCEPTED
PACKET REJECTED
63
0
6
64
LOGICAL
ADDRESS
FILTER
(LADRF)
32-BIT RESULTANT CRC
MATCH
MATCH=1:
PACKET ACCEPTED
MATCH=0:
PACKET REJECTED
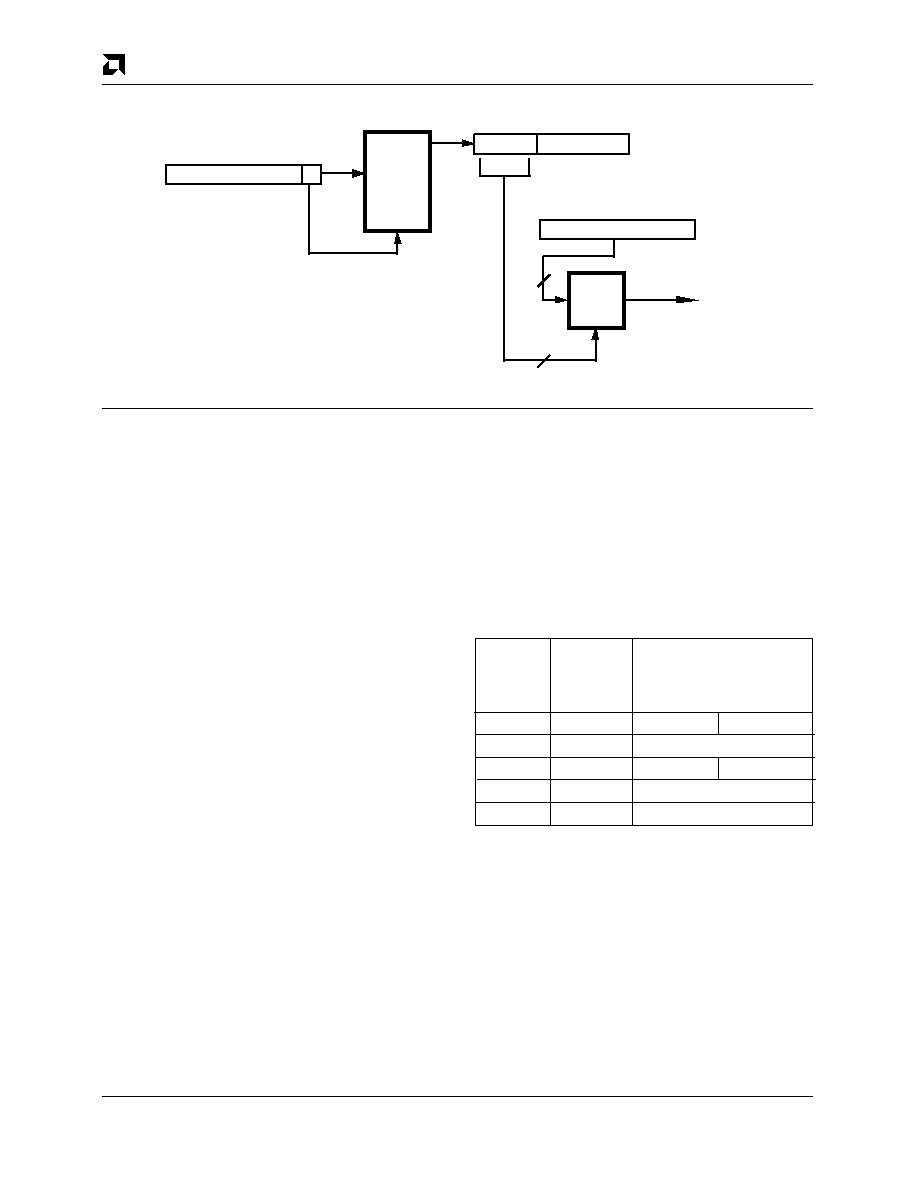
Figure 38. Address Match Logic
The Logical Address Filter is used in multicast address-
ing schemes. The acceptance of the incoming frame
based on the filter value indicates that the message may
be intended for the node. It is the node’s responsibility to
determine if the message is actually intended for the
node by comparing the destination address of the stored
message with a list of acceptable logical addresses.
If the Logical Address Filter is loaded with all zeroes and
promiscuous mode is disabled, all incoming logical ad-
dresses except broadcast will be rejected.
The Broadcast address, which is all ones, does not go
through the Logical Address Filter and is handled as
follows:
s If the Disable Broadcast Bit is cleared, the broadcast
address is accepted
s If the Disable Broadcast Bit is set and promiscuous
mode is enabled, the broadcast address is accepted.
s If the Disable Broadcast Bit is set and promiscuous
mode is disabled, the broadcast address is rejected.
If external loopback is used, the FCS logic must be allo-
cated to the receiver (by setting the DXMTFCS bit in
CSR15, and clearing the ADD_FCS bit in TMD1) when
using multicast addressing.
PADR
This 48-bit value represents the unique node address
assigned by the ISO 8802-3 (IEEE/ANSI 802.3) and
used for internal address comparison. PADR[0] is the
first address bit transmitted on the wire, and must be
zero. The six hex-digit nomenclature used by the ISO
8802-3 (IEEE/ANSI 802.3) maps to the PCnet-32 con-
troller PADR register as follows: the first byte comprises
PADR[7:0], with PADR[0] being the least significant bit
of the byte. The second ISO 8802-3 (IEEE/ANSI 802.3)
byte maps to PADR[15:8], again from LS bit to MS bit,
and so on. The sixth byte maps to PADR[47:40], the LS
bit being PADR[40].
MODE
The mode register in the initialization block is copied into
CSR15 and interpreted according to the description of
CSR15.
Receive Descriptors
When SSIZE32 = 0 (BCR20[8]), then the software struc-
tures are defined to be 16 bits wide, and receive descrip-
tors look as shown in Table 59.
Table 59. Receive Descriptor (SSIZE32 = 0)
Descriptor
Designation
Address
Bits 15-0
Bits 15-8
Bits 7-0
CRDA+00
RMD0
RMD0[15:0]
CRDA+02
RMD1
RMD1[31:24]
RMD0[23:16]
CRDA+04
RMD2
RMD1[15:0]
CRDA+06
RMD3
RMD2[15:0]
PCnet-32
Descriptor Designation
LANCE/
PCnet-ISA
PCnet-32 reference names within the table above refer
to the descriptor definitions given in text below. Since
the text descriptions are for 32-bit descriptors, the table
above shows the mapping of the 32-bit descriptors into
the 16-bit descriptor space. Since 16-bit descriptors are
a subset of the 32-bit descriptors, some portions of the
32-bit descriptors may not appear in Table 59.
When SSIZE32 = 1 (BCR 20[8]), then the software
structures are defined to be 32 bits wide, and receive
descriptors look as shown in Table 60.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AM80A-024L-120F18 | 1-OUTPUT 240 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| AJ80A-024L-033F50 | 1-OUTPUT 240 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| AM93LC66S | 4096-bits Serial Electrically Erasable PROM |
| AM93LC66SA | 4096-bits Serial Electrically Erasable PROM |
| AM93LC66VN | 4096-bits Serial Electrically Erasable PROM |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| AM79C970 | 制造商:AMD 制造商全稱:Advanced Micro Devices 功能描述:PCnetTM-PCI Single-Chip Ethernet Controller for PCI Local Bus |
| AM79C970A | 制造商:AMD 制造商全稱:Advanced Micro Devices 功能描述:PCnet-PCI II Single-Chip Full-Duplex Ethernet Controller for PCI Local Bus Product |
| AM79C970AKC | 制造商:AMD 制造商全稱:Advanced Micro Devices 功能描述:PCnet-PCI II Single-Chip Full-Duplex Ethernet Controller for PCI Local Bus Product |
| AM79C970AKC\\W | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk 制造商:Advanced Micro Devices 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。